DADA SOM/DADA Hardware/pdf
General Information[edit | edit source]
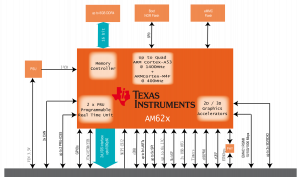
DADA Block Diagram[edit | edit source]
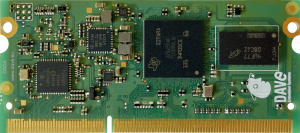
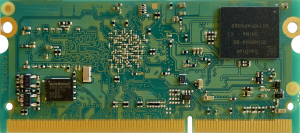
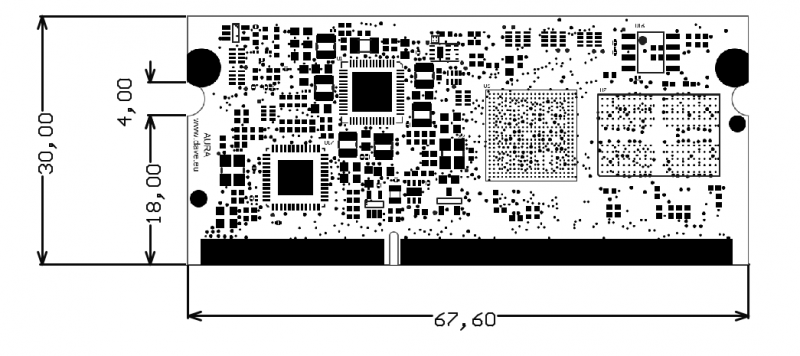
DADA TOP View[edit | edit source]
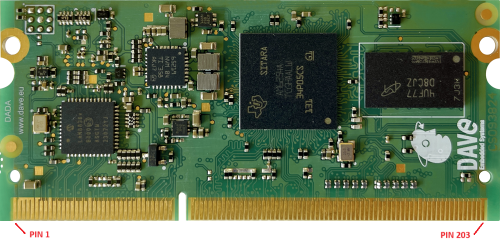
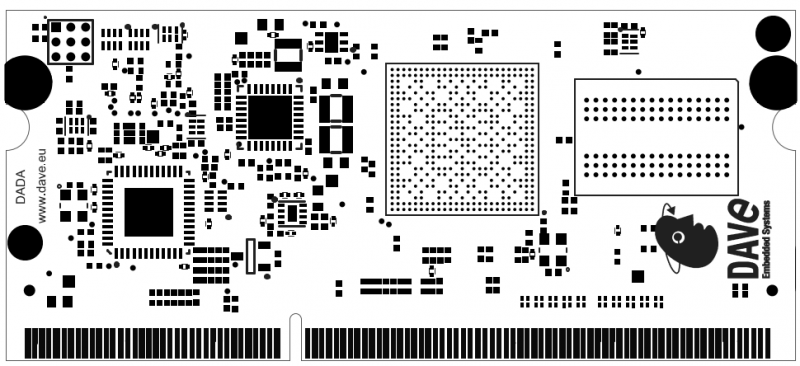
DADA BOTTOM View[edit | edit source]
Processor and memory subsystem[edit | edit source]
The heart of DADA module is composed by the following components:
- AM62x SoC application processor
- Power supply unit
- DDR4 memory bank
- eMMC storage device
- Connectors:
- 1 x 204 pins SO-DIMM edge connector with interfaces signals
- partially compatible with AXEL Lite SOM
- 1 x 204 pins SO-DIMM edge connector with interfaces signals
This chapter shortly describes the main DADA components.
Processor Info[edit | edit source]
| Processor | AM62x SingleCore | AM62x DualCore | AM62x Quadcore |
| # Cores | 1x Arm® Cortex®-A53
1x Arm® Cortex®-M4F |
2x Arm® Cortex®-A53
1x Arm® Cortex®-M4F |
4x Arm® Cortex®-A53
1x Arm® Cortex®-M4F |
| Clock | Core: 1.4 GHz (Industrial)
Cortex-M4F: up to 400 MHz | ||
| L2
Cache |
512KB MB | ||
| DDR4 | 16 bit
(1600MT/s) | ||
| GPU | 3D: PowerVR AXE-1-16M
OpenGL ES 3.1 | ||
| PRUSS | Dual core Programmable Real-Time Unit Subystem
up to 333 MHz | ||
| Display
Controller |
Dual independent LVDS channel
2x 1920x1080@60 or 1x 2048x1080 + 1x 1280x720 | ||
| Video
Output |
Dual LVDS channel 24-bit RGB DPI | ||
| Camera
Input |
1x MIPI CSI (4-lanes) | ||
| Ethernet | 2x 10/100/1000 Mbit/s controller with TSN and IEEE1588 | ||
| USB | 2x USB 2.0 Host or Device DRD (Dual-Role Device) | ||
RAM memory bank[edit | edit source]
LPDD4 SDRAM memory bank is composed by 1x16-bit width chip. The following table reports the SDRAM specifications:
| CPU connection | DDR subsystem (DDRSS) |
| Size max | 8 GB |
| Width | 16 bit |
| Speed | 1600 MHz |
eMMC storage[edit | edit source]
On board main storage memory eMMC is connected to the MMC0 interface and it can act as boot peripheral. The following table reports the eMMC flash specifications:
| CPU connection | MMC0 |
| Size min | 8 GB |
| Size max | 64 GB |
| Bootable | Yes |
NOR QSPI flash[edit | edit source]
Alternative option for main storage memory can be a serial NOR flash connected to the CPU's Quad serial flash controller. It can act as boot peripheral. The following table reports the NOR flash specifications:
| CPU connection | SPI Serial flash controller |
| Size | 16GB |
| Width | 1,4 bit mode |
| Bootable | Yes |
Memory map[edit | edit source]
For detailed information, please refer to chapter 9.1 “Memory Controllers” of the AM62x Processor Technical Reference Manual
Power supply unit[edit | edit source]
DADA embeds all the elements required for powering the unit, therefore power sequencing is self-contained and simplified. Nevertheless, power must be provided from carrier board, and therefore users should be aware of the ranges power supply can assume as well as all other parameters.
Hardware versioning and tracking[edit | edit source]
DAD SOM implements well established versioning and tracking mechanisms:
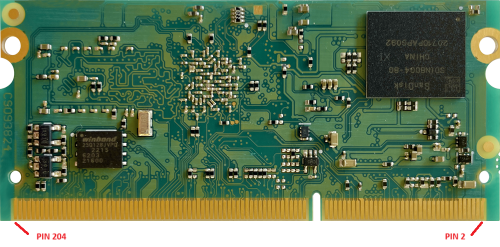
- PCB version is copper printed on PCB itself, as shown in Fig. 1
- serial number: it is printed on a white label, as shown in Fig. 2: see also Product serial number page for more details
- ConfigID: it is used by software running on the board for the identification of the product model/hardware configuration. For more details, please refer to this link
- on DADA SOM ConfigID is stored in (TBD)
Part number composition[edit | edit source]
DADA SOM module part number is identified by the following digit-code table:
| Part number structure | Options | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Family | DSAA | Family prefix code |
| SOC |
|
Other versions can be available, please contact technical support |
| RAM |
|
|
| Storage |
|
|
| Boot mode |
|
|
| Mounting options |
|
|
| RFU |
|
Reserved for Future Use |
| Temperature range |
|
|
| PCB revision |
|
PCB release may change for manufacturing purposes (i.e. text fixture adaptation) |
| Manufacturing option |
|
typically connected to production process and quality |
| Software Configuration | -00: standard factory u-boot pre-programmed | If customers require custom SW deployed this section should be defined and agreed. Please contact technical support |
Example[edit | edit source]
DADA SOM code DSAAA13100I0R-00
- DSAA - DADA
- A - Texas Instruments AM6254ATCGHAALW Arm A53 QuadCore, PRU, GPU @1.4GHz
- 1 - 2GB DDR4
- 3 - 8GB eMMC
- 1 - Boot from on board eMMC
- 0 - 3.3V high performance PMIC
- 0 - RFU
- I - Industrial grade: -40 to 85°C
- 0 - first version
- R - RoHS
- -00 - standard factory u-boot pre-programmed
Pinout Table[edit | edit source]
Connector and Pinout Table[edit | edit source]
Connector description[edit | edit source]
In the following table are described all available connector integrated on DADA:
| Connector name | Connector Type | Notes | Carrier board counterpart |
|---|---|---|---|
| J1 | SODIMM DDR3 edge connector 204 pin | TE Connectivity 2-2013289-1 |
The dedicated carrier board must mount the mating connector and connect the desired peripheral interfaces according to DADA pinout specifications. See the images below for reference:
Pinout table naming conventions[edit | edit source]
This chapter contains the pinout description of the DADA module, grouped in two tables (odd and even pins) that report the pin mapping of the 204-pin SO-DIMM DADA connector.
Each row in the pinout tables contains the following information:
| Pin | Reference to the connector J1 pin |
| Pin type | Pin topolgy according to Unica Industrial Dave standard:
|
| UNICA pin name | Pin name according to Unica Industrial Dave standard |
| Type | Electrical pin type:
|
| DADA pin name | Pin (signal) name on the DADA J1 connector.
In bold if it covers a UNICA pinout feature. |
| Internal connections |
Connections to the DADA components:
|
| Ball/pin # | Component ball/pin number connected to signal |
| SoM voltage domain | I/O voltage levels (SoM main rails) |
| SoC voltage domain | I/O voltage levels (all voltage rails) |
| Notes | Remarks on special pin characteristics |
| Pin MUX mode | Muxes:
In bold the mux applied in the standard device-tree to cover a UNICA pinout functionality. |
SoM voltage domains[edit | edit source]
| Voltage domain | Nominal voltage | Source | Peripheral PWR | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN_SOM | 3.3 V | External | SoM input PWR | See Operational_characteristics of the SoM wiki page |
| VDD_3V3 | 3.3 V | Internal | IO | Voltage generated by the internal PSU. |
| VDD_1V8 | 1.8 V | Internal | IO | Voltage generated by the internal PSU. |
| VDD_RGMII | 3.3 V | Internal | RGMII | It can be set to 1.8 V with HW mounting option. |
| MMC2_POWER | 1.8 V o 3.3 V | External | MMC2 | Voltage generated by the carrier board PSU, synchronous with SOM_PGOOD signal. |
For more details and recommended power-up sequence see Power Supply Unit (PSU) wiki page.
Pinout choice[edit | edit source]
It is not possible to bring all the SoC pins to the J1 connector. The mapping choice was made in order to respect:
- cover always-present and variable peripherals mapped in the Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout
- bring out all SoC peripherals of the MCU, CANUART and PRU domain
- bring out all pins with BOOTMODE function
Pinout table XLS file[edit | edit source]
For your convenience, please find a spreadsheet with:
Pinout Table ODD pins declaration[edit | edit source]
| Pin | Pin Type | UNICA pin name | Type | DADA pin name | Internal Connections | Ball/pin # | SoM Voltage domain | SoC Voltage domain | Notes | Boot Mode | Alternative mux modes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J2.1 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.3 | AP | VIN_SOM | PWR | VIN_SOM | VIN_SOM | ||||||||
| J2.5 | AP | VIN_SOM | PWR | VIN_SOM | VIN_SOM | ||||||||
| J2.7 | AP | VIN_SOM | PWR | VIN_SOM | VIN_SOM | ||||||||
| J2.9 | AP | VIN_SOM | PWR | VIN_SOM | VIN_SOM | ||||||||
| J2.11 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.13 | AP | ETH_A_LED1 | S | O | ETH1_LED1 | LAN | 18 | VDD_3V3 | |||||
| J2.15 | AP | ETH_A_LED2 | S | O | ETH1_LED2 | LAN | 16 | VDD_3V3 | |||||
| J2.17 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.19 | AP | ETH_A_TXRX0_P | D | IO | ETH1_TXRX0_P | LAN | 2 | VDD_3V3 | |||||
| J2.21 | AP | ETH_A_TXRX0_N | D | IO | ETH1_TXRX0_N | LAN | 3 | VDD_3V3 | |||||
| J2.23 | AP | ETH_A_TXRX1_P | D | IO | ETH1_TXRX1_P | LAN | 5 | VDD_3V3 | |||||
| J2.25 | AP | ETH_A_TXRX1_N | D | IO | ETH1_TXRX1_N | LAN | 6 | VDD_3V3 | |||||
| J2.27 | AP | ETH_A_TXRX2_P | D | IO | ETH1_TXRX2_P | LAN | 7 | VDD_3V3 | |||||
| J2.29 | AP | ETH_A_TXRX2_N | D | IO | ETH1_TXRX2_N | LAN | 8 | VDD_3V3 | |||||
| J2.31 | AP | ETH_A_TXRX3_P | D | IO | ETH1_TXRX3_P | LAN | 10 | VDD_3V3 | |||||
| J2.33 | AP | ETH_A_TXRX3_N | D | IO | ETH1_TXRX3_N | LAN | 11 | VDD_3V3 | |||||
| J2.35 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.37 | VAR | VAR_A_37 | S | IO | GPMC0_WP# | SoC | K25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_WP# | ||
| ALT-1 | AUDIO_EXT_REFCLK1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | GPMC0_A22 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART6_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO15 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI15 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA13 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_39 | ||||||||||||
| J2.37 | VAR | VAR_A_37 (*) | S | O | ETH1_LED3 | LAN | 15 | VDD_3V3 | Hardware mounting option (*) | ||||
| J2.39 | VAR | VAR_A_39 | S | IO | GPMC0_DIR | SoC | M22 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_DIR | ||
| ALT-1 | PR0_ECAP0_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR13 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO16 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI16 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA14 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_40 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP2_S | ||||||||||||
| J2.39 | VAR | VAR_A_39 (*) | S | O | ETH1_LED4 | LAN | 14 | VDD_3V3 | Hardware mounting option (*) | ||||
| J2.39 | VAR | VAR_A_39 (*) | S | O | ETH1_LED5 | LAN | 13 | VDD_3V3 | Hardware mounting option (*) | ||||
| J2.41 | VAR | VAR_A_41 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD03 | SoC | N25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE03 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD3 | |
| ALT-1 | PR0_PRU1_GPO11 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPI11 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR7 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_18 | ||||||||||||
| J2.43 | VAR | VAR_A_43 | S | IO | MCU_UART0_TXD | SoC | A5 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | MCU_UART0_TXD | ||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_6 | ||||||||||||
| J2.45 | VAR | VAR_A_45 | S | IO | MCU_UART0_RXD | SoC | B5 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | MCU_UART0_RXD | ||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_5 | ||||||||||||
| J2.47 | VAR | UART_B_TX | S | IO | VOUT_DATA5 | SoC | Y24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | VOUT0_DATA5 | ||
| ALT-1 | GPMC0_A5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPO5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPI5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART4_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPO13 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_PRU0_GPI13 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_50 | ||||||||||||
| J2.49 | VAR | UART_B_RX | S | IO | VOUT_DATA4 | SoC | Y25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | VOUT0_DATA4 | ||
| ALT-1 | GPMC0_A4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPO4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPI4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART4_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPO12 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_PRU0_GPI12 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_49 | ||||||||||||
| J2.51 | VAR | UART_B_RTS | S | IO | VOUT_DATA14 | SoC | Y22 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | VOUT0_DATA14 | ||
| ALT-1 | GPMC0_A14 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPO13 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPI13 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART4_RTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPO4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_PRU0_GPI4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_59 | ||||||||||||
| J2.53 | VAR | UART_B_CTS | S | IO | VOUT_DATA15 | SoC | AA21 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | VOUT0_DATA15 | ||
| ALT-1 | GPMC0_A15 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPO14 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPI14 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART4_CTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPO5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_PRU0_GPI5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_60 | ||||||||||||
| J2.55 | VAR | VAR_A_55 | S | IO | PMIC_INT | SoC | M24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | Internal 10K pull-up | ALT-0 | GPMC0_BE0_CLE# | |
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_ACLKX | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO12 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI12 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA10 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_35 | ||||||||||||
| J2.57 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.59 | VAR | SDIO_B_PWR | PWR | MMC2_POWER | SoC | J18 | MMC2_POWER | VDDSHV6 | |||||
| J2.61 | AP | SDIO_B_DATA0 | S | IO | MMC2_DAT0 | SoC | B24 | MMC2_POWER | VDDSHV6 | ALT-0 | MMC2_DAT0 | ||
| ALT-1 | MCASP1_AXR0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_68 | ||||||||||||
| J2.63 | AP | SDIO_B_DATA1 | S | IO | MMC2_DAT1 | SoC | C25 | MMC2_POWER | VDDSHV6 | ALT-0 | MMC2_DAT1 | ||
| ALT-1 | MCASP1_AXR1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_67 | ||||||||||||
| J2.65 | AP | SDIO_B_DATA2 | S | IO | MMC2_DAT2 | SoC | E23 | MMC2_POWER | VDDSHV6 | ALT-0 | MMC2_DAT2 | ||
| ALT-1 | MCASP1_AXR2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART5_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_66 | ||||||||||||
| J2.67 | AP | SDIO_B_DATA3 | S | IO | MMC2_DAT3 | SoC | D24 | MMC2_POWER | VDDSHV6 | ALT-0 | MMC2_DAT3 | ||
| ALT-1 | MCASP1_AXR3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART5_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_65 | ||||||||||||
| J2.69 | AP | SDIO_B_CMD | S | IO | MMC2_CMD | SoC | C24 | MMC2_POWER | VDDSHV6 | ALT-0 | MMC2_CMD | ||
| ALT-1 | MCASP1_AFSR | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_AXR4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART6_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_70 | ||||||||||||
| J2.71 | AP | SDIO_B_CLK | S | O | MMC2_CLK | SoC | D25 | MMC2_POWER | VDDSHV6 | ALT-0 | MMC2_CLK | ||
| ALT-1 | MCASP1_ACLKR | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_AXR5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART6_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_69 | ||||||||||||
| J2.73 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.75 | AP | SDIO_A_DATA0 | S | IO | MMC1_DAT0 | SoC | A22 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV5 | ALT-0 | MMC1_DAT0 | ||
| ALT-1 | CP_GEMAC_CPTS0_HW2TSPUSH | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART2_CTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | ECAP2_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_45 | ||||||||||||
| J2.77 | AP | SDIO_A_DATA1 | S | IO | MMC1_DAT1 | SoC | B21 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV5 | ALT-0 | MMC1_DAT1 | ||
| ALT-1 | CP_GEMAC_CPTS0_HW1TSPUSH | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART2_RTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | ECAP1_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_44 | ||||||||||||
| J2.79 | AP | SDIO_A_DATA2 | S | IO | MMC1_DAT2 | SoC | C21 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV5 | ALT-0 | MMC1_DAT2 | ||
| ALT-1 | CP_GEMAC_CPTS0_TS_SYNC | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART2_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_43 | ||||||||||||
| J2.81 | AP | SDIO_A_DATA3 | S | IO | MMC1_DAT3 | SoC | D22 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV5 | ALT-0 | MMC1_DAT3 | ||
| ALT-1 | CP_GEMAC_CPTS0_TS_COMP | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART2_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_42 | ||||||||||||
| J2.83 | AP | SDIO_A_CMD | S | IO | MMC1_CMD | SoC | A21 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV5 | ALT-0 | MMC1_CMD | ||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART3_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_47 | ||||||||||||
| J2.85 | AP | SDIO_A_CLK | S | O | MMC1_CLK | SoC | B22 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV5 | ALT-0 | MMC1_CLK | ||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART3_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_46 | ||||||||||||
| J2.87 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.89 | VAR | VAR_B_89 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD11 | SoC | R21 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE11 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD11 | |
| ALT-1 | VOUT0_DATA19 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART3_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU1_GPO3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU1_GPI3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA23 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_26 | ||||||||||||
| J2.91 | VAR | VAR_B_91 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD10 | SoC | T25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE10 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD10 | |
| ALT-1 | VOUT0_DATA18 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART3_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU1_GPO2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU1_GPI2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_25 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | OBSCLK0 | ||||||||||||
| J2.93 | AP | UART_C_TX | S | IO | GPMC0_AD09 | SoC | R25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE09 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD9 | |
| ALT-1 | VOUT0_DATA17 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART2_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU1_GPO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU1_GPI1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_24 | ||||||||||||
| J2.95 | AP | UART_C_RX | S | IO | GPMC0_AD08 | SoC | R24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE08 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD8 | |
| ALT-1 | VOUT0_DATA16 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART2_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU1_GPO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU1_GPI0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_23 | ||||||||||||
| J2.97 | VAR | VAR_B_97 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD13 | SoC | T24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE13 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD13 | |
| ALT-1 | VOUT0_DATA21 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART4_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_ACLKX | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA21 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_28 | ||||||||||||
| J2.99 | VAR | VAR_B_99 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD12 | SoC | T22 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE12 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD12 | |
| ALT-1 | VOUT0_DATA20 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART4_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AFSX | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA22 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_27 | ||||||||||||
| J2.101 | AP | I2C_A_SCL | S | IO | GPMC0_CS2# | SoC | K22 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | CMOS | ALT-0 | GPMC0_CS2# | |
| ALT-1 | I2C2_SCL | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_AXR4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART4_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO19 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI19 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA17 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_43 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | MCASP1_AFSR | ||||||||||||
| J2.103 | AP | I2C_A_SDA | S | IO | GPMC0_CS3# | SoC | K24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | CMOS | ALT-0 | GPMC0_CS3# | |
| ALT-1 | I2C2_SDA | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | GPMC0_A20 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART4_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | MCASP1_AXR5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA18 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_44 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | MCASP1_ACLKR | ||||||||||||
| J2.105 | VAR | VAR_B_105 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD15 | SoC | U24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE15 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD15 | |
| ALT-1 | VOUT0_DATA23 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART5_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_ACLKR | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA19 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_30 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | UART2_RTSn | ||||||||||||
| J2.107 | VAR | VAR_B_107 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD14 | SoC | U25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE14 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD14 | |
| ALT-1 | VOUT0_DATA22 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART5_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AFSR | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA20 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_29 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | UART2_CTSn | ||||||||||||
| J2.109 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.111 | VAR | VAR_A_111 | S | IO | MCASP0_AXR1 | SoC | B18 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MCASP0_AXR1 | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI2_CS2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | ECAP1_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_UART0_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | EHRPWM1_A | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_9 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP0_S | ||||||||||||
| J2.113 | VAR | VAR_A_113 | S | IO | SPI0_CS1 | SoC | C13 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | SPI0_CS1 | ||
| ALT-1 | CP_GEMAC_CPTS0_TS_COMP | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | EHRPWM0_B | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | ECAP0_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_16 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-9 | EHRPWM_TZn_IN5 | ||||||||||||
| J2.115 | VAR | VAR_A_115 | OD | IO | MCU_I2C0_SCL | SoC | A8 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | Internal 4K7 pull-up | ALT-0 | MCU_I2C0_SCL | |
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_17 | ||||||||||||
| J2.117 | VAR | VAR_A_117 | OD | IO | MCU_I2C0_SDA | SoC | D10 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | Internal 4K7 pull-up | ALT-0 | MCU_I2C0_SDA | |
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_18 | ||||||||||||
| J2.119 | AP | GPIO_IRQ_A | S | IO | UART0_RTS# | SoC | B15 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | UART0_RTSn | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI0_CS3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | I2C3_SDA | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART2_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | TIMER_IO7 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | AUDIO_EXT_REFCLK1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_ECAP0_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_23 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | MCASP2_ACLKX | ||||||||||||
| ALT-9 | MMC2_SDWP | ||||||||||||
| J2.121 | AP | GPIO_IRQ_B | S | IO | SPI0_D1 | SoC | B14 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | SPI0_D1 | ||
| ALT-1 | CP_GEMAC_CPTS0_HW2TSPUSH | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | EHRPWM_TZn_IN0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_19 | ||||||||||||
| J2.123 | AP | GPIO_A | S | IO | SPI0_D0 | SoC | B13 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | SPI0_D0 | ||
| ALT-1 | CP_GEMAC_CPTS0_HW1TSPUSH | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | EHRPWM1_B | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_18 | ||||||||||||
| J2.125 | AP | GPIO_B | S | IO | MCASP0_ACLKR | SoC | A20 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MCASP0_ACLKR | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI2_CLK | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART1_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | EHRPWM0_B | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_14 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP1_I | ||||||||||||
| J2.127 | VAR | VAR_A_127 | S | IO | VOUT_DATA12 | SoC | AB25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | VOUT0_DATA12 | ||
| ALT-1 | GPMC0_A12 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPO11 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPI11 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART5_RTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPO2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_PRU0_GPI2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_57 | ||||||||||||
| J2.129 | VAR | VAR_A_129 | S | IO | GPMC0_WAIT1 | SoC | V25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_WAIT1 | ||
| ALT-1 | VOUT0_EXTPCLKIN | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | GPMC0_A21 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART6_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_38 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP2_I | ||||||||||||
| J2.131 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.133 | AP | LVDS_A_CLK_N | D | O | OLDI0_CLK0_N | SoC | AD4 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_CLK0_N | |||
| J2.135 | AP | LVDS_A_CLK_P | D | O | OLDI0_CLK0_P | SoC | AE3 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_CLK0_P | |||
| J2.137 | AP | LVDS_A_TX0_N | D | O | OLDI0_A0_N | SoC | AA5 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A0_N | |||
| J2.139 | AP | LVDS_A_TX0_P | D | O | OLDI0_A0_P | SoC | Y6 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A0_P | |||
| J2.141 | AP | LVDS_A_TX1_N | D | O | OLDI0_A1_N | SoC | AD3 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A1_N | |||
| J2.143 | AP | LVDS_A_TX1_P | D | O | OLDI0_A1_P | SoC | AB4 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A1_P | |||
| J2.145 | AP | LVDS_A_TX2_N | D | O | OLDI0_A2_N | SoC | Y8 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A2_N | |||
| J2.147 | AP | LVDS_A_TX2_P | D | O | OLDI0_A2_P | SoC | AA8 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A2_P | |||
| J2.149 | AP | LVDS_A_TX3_N | D | O | OLDI0_A3_N | SoC | AB6 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A3_N | |||
| J2.151 | AP | LVDS_A_TX3_P | D | O | OLDI0_A3_P | SoC | AA7 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A3_P | |||
| J2.153 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.155 | VAR | VAR_DIF_A_155 | D | O | OLDI0_CLK1_N | SoC | AE4 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_CLK1_N | |||
| J2.157 | VAR | VAR_DIF_A_157 | D | O | OLDI0_CLK1_P | SoC | AD5 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_CLK1_P | |||
| J2.159 | VAR | VAR_DIF_A_159 | D | O | OLDI0_A4_N | SoC | AC6 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A4_N | |||
| J2.161 | VAR | VAR_DIF_A_161 | D | O | OLDI0_A4_P | SoC | AC5 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A4_P | |||
| J2.163 | VAR | VAR_DIF_A_163 | D | O | OLDI0_A5_N | SoC | AE5 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A5_N | |||
| J2.165 | VAR | VAR_DIF_A_165 | D | O | OLDI0_A5_P | SoC | AD6 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A5_P | |||
| J2.167 | VAR | VAR_DIF_A_167 | D | O | OLDI0_A6_N | SoC | AE6 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A6_N | |||
| J2.169 | VAR | VAR_DIF_A_169 | D | O | OLDI0_A6_P | SoC | AD7 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A6_P | |||
| J2.171 | VAR | VAR_DIF_A_171 | D | O | OLDI0_A7_N | SoC | AD8 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A7_N | |||
| J2.173 | VAR | VAR_DIF_A_173 | D | O | OLDI0_A7_P | SoC | AE7 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_OLDI | OLDI0_A7_P | |||
| J2.175 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.177 | AP | SDIO_A_CardDetect | S | I | MMC1_SDCD | SoC | D17 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MMC1_SDCD | ||
| ALT-1 | UART6_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO6 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART3_RTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_48 | ||||||||||||
| J2.179 | AP | SPI_A_SS0 | S | IO | OSPI0_D4 | SoC | J23 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV1 | ALT-0 | OSPI0_D4 | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI1_CS0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_AXR1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART6_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_7 | ||||||||||||
| J2.181 | AP | SPI_A_SCLK | S | IO | OSPI0_D5 | SoC | J25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV1 | ALT-0 | OSPI0_D5 | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI1_CLK | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_AXR0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART6_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_8 | ||||||||||||
| J2.183 | AP | SPI_A_MISO | S | IO | OSPI0_D7 | SoC | J22 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV1 | ALT-0 | OSPI0_D7 | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI1_D1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_AFSX | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART6_CTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_10 | ||||||||||||
| J2.185 | AP | SPI_A_MOSI | S | IO | OSPI0_D6 | SoC | H25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV1 | ALT-0 | OSPI0_D6 | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI1_D0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_ACLKX | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART6_RTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | GPIO0_9 | ||||||||||||
| J2.187 | AP | UART_A_TX | S | IO | UART0_TXD | SoC | E14 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | UART0_TXD | ||
| ALT-1 | ECAP2_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | SPI2_D1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | EHRPWM2_B | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_21 | ||||||||||||
| J2.189 | AP | UART_A_RX | S | IO | UART0_RXD | SoC | D14 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | UART0_RXD | ||
| ALT-1 | ECAP1_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | SPI2_D0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | EHRPWM2_A | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_20 | ||||||||||||
| J2.191 | VAR | VAR_B_191 | S | IO | OSPI0_CS2# | SoC | H21 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV1 | ALT-0 | OSPI0_CSn2 | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI1_CS1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | OSPI0_RESET_OUT1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP1_AFSR | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | MCASP1_AXR2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | UART5_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_13 | ||||||||||||
| J2.193 | VAR | VAR_A_193 | S | IO | WKUP_UART0_TXD | SoC | C5 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | WKUP_UART0_TXD | ||
| ALT-2 | MCU_SPI1_CS2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_10 | ||||||||||||
| J2.195 | VAR | VAR_A_195 | S | IO | WKUP_UART0_RXD | SoC | B4 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | WKUP_UART0_RXD | ||
| ALT-2 | MCU_SPI0_CS2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_9 | ||||||||||||
| J2.197 | VAR | VAR_A_197 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD00 | SoC | M25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE00 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD0 | |
| ALT-1 | PR0_PRU1_GPO8 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPI8 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_CLK | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_15 | ||||||||||||
| J2.199 | VAR | VAR_A_199 | S | IO | MCASP0_AFSR | SoC | E19 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MCASP0_AFSR | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI2_CS0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART1_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | EHRPWM0_A | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_13 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP1_S | ||||||||||||
| J2.201 | VAR | VAR_A_201 | S | IO | GPMC0_WE# | SoC | L25 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_WEn | ||
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_AXR0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO11 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI11 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA9 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_34 | ||||||||||||
| J2.203 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
Pinout Table ODD pins declaration[edit | edit source]
| Pin | Pin Type | UNICA pin name | Type | DADA pin name | Internal Connections | Ball/pin # | SoM Voltage domain | SoC Voltage domain | Notes | Boot Mode | Alternative mux modes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J2.2 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.4 | AP | VIN_SOM | PWR | +VIN_SOM | VIN_SOM | ||||||||
| J2.6 | AP | VIN_SOM | PWR | +VIN_SOM | VIN_SOM | ||||||||
| J2.8 | AP | VIN_SOM | PWR | +VIN_SOM | VIN_SOM | ||||||||
| J2.10 | AP | VIN_SOM | PWR | +VIN_SOM | VIN_SOM | ||||||||
| J2.12 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.14 | VAR | WARM_RESET | OD | I | WARM_RESET | RST | - | VDD_3V3 | Internal 10K pull-upll-up | ||||
| J2.16 | VAR | ONOFF_STDBY | OD | I | ONOFF_STDBY | PMIC | 25 | VIN_SOM | Internal 10K pull-upll-up | ||||
| J2.18 | AP | SOM_PGOOD | PP | O | SOM_PGOOD | VM | - | VIN_SOM | |||||
| J2.20 | AP | BOOT_MODE_SEL | OD | I | BOOT_MODE_SEL | BOOT | - | VDD_3V3 | Internal 10K pull-up | ||||
| J2.22 | VAR | POR_OUT | OD | O | POR_OUT | RST | - | VIN_SOM | Pull-up on the carrier | ||||
| J2.24 | AP | COLD_RESET | OD | I | COLD_RESET | RST | - | VDD_3V3 | Internal 10K pull-up | ||||
| J2.26 | VAR | VAR_B_26 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD01 | SoC | N23 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE01 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD1 | |
| ALT-1 | PR0_PRU1_GPO9 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPI9 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_CTL | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_16 | ||||||||||||
| J2.28 | AP | PWM_A | S | O | SPI0_CS0 | SoC | A13 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | SPI0_CS0 | ||
| ALT-2 | EHRPWM0_A | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_ECAP0_SYNC_IN | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_15 | ||||||||||||
| J2.30 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.32 | VAR | VAR_B_32 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD07 | SoC | R23 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE07 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD7 | |
| ALT-1 | PR0_PRU1_GPO15 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPI15 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR11 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO7 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI7 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_22 | ||||||||||||
| J2.34 | VAR | VAR_B_34 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD04 | SoC | P24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE04 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD4 | |
| ALT-1 | PR0_PRU1_GPO12 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPI12 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR8 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_19 | ||||||||||||
| J2.36 | VAR | VAR_B_36 | S | IO | SPI0_CLK | SoC | A14 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | SPI0_CLK | ||
| ALT-1 | CP_GEMAC_CPTS0_TS_SYNC | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | EHRPWM1_A | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | GPIO1_17 | ||||||||||||
| J2.38 | AP | I2C_B_SCL | S | O | I2C1_SCL | SoC | B17 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | Internal Internal 4K7 pull-upll-up, CMOS | ALT-0 | I2C1_SCL | |
| ALT-1 | UART1_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | SPI2_CS1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | EHRPWM0_SYNCI | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_28 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EHRPWM2_A | ||||||||||||
| ALT-9 | MMC2_SDCD | ||||||||||||
| J2.40 | AP | I2C_B_SDA | S | IO | I2C1_SDA | SoC | A17 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | Internal Internal 4K7 pull-upll-up, CMOS | ALT-0 | I2C1_SDA | |
| ALT-1 | UART1_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | SPI2_CLK | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | EHRPWM0_SYNCO | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_29 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EHRPWM2_B | ||||||||||||
| ALT-9 | MMC2_SDWP | ||||||||||||
| J2.42 | AP | CAN_A_TX | S | O | MCAN0_TX | SoC | C15 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MCAN0_TX | ||
| ALT-1 | UART5_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | SYNC2_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART1_DTRn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | EQEP2_I | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_UART0_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_24 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | MCASP2_AXR0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-9 | EHRPWM_TZn_IN3 | ||||||||||||
| J2.44 | AP | CAN_A_RX | S | I | MCAN0_RX | SoC | E15 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MCAN0_RX | ||
| ALT-1 | UART5_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | TIMER_IO3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | SYNC3_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART1_RIn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | EQEP2_S | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_UART0_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_25 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | MCASP2_AXR1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-9 | EHRPWM_TZn_IN4 | ||||||||||||
| J2.46 | VAR | VAR_B_46 | S | I | JTAG_TRST | SoC | B10 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | Internal 10K pull-down | TRSTN | ||
| J2.48 | AP | JTAG_TDI | S | I | JTAG_TDI | SoC | A11 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | TDI | |||
| J2.50 | AP | JTAG_TMS | S | I | JTAG_TMS | SoC | B11 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | TMS | |||
| J2.52 | AP | JTAG_TCK | S | I | JTAG_TCK | SoC | A10 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | TCK | |||
| J2.54 | AP | JTAG_TDO | S | O | JTAG_TDO | SoC | D12 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | TDO | |||
| J2.56 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.58 | VAR | VAR_B_58 | S | IO | MCU_MCAN0_TX | SoC | D6 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | MCU_MCAN0_TX | ||
| ALT-1 | WKUP_TIMER_IO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCU_SPI0_CS3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_13 | ||||||||||||
| J2.60 | VAR | VAR_B_60 | S | IO | MCU_MCAN0_RX | SoC | B3 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | MCU_MCAN0_RX | ||
| ALT-1 | MCU_TIMER_IO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCU_SPI1_CS3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_14 | ||||||||||||
| J2.62 | AP | CONFIG_ID (1wire) | S | IO | CB_CONFIG_ID | 1wM | - | ||||||
| J2.64 | AP | Audio_MCLK | S | O | UART0_CTS# | SoC | A15 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | UART0_CTSn | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI0_CS2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | I2C3_SCL | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART2_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | TIMER_IO6 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | AUDIO_EXT_REFCLK0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_ECAP0_SYNC_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_22 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | MCASP2_AFSX | ||||||||||||
| ALT-9 | MMC2_SDCD | ||||||||||||
| J2.66 | AP | Audio_BCLK | S | O | MCASP0_ACLKX | SoC | B20 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MCASP0_ACLKX | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI2_CS1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | ECAP2_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_11 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP1_A | ||||||||||||
| J2.68 | AP | Audio_DOUT | S | O | MCASP0_AXR0 | SoC | E18 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MCASP0_AXR0 | ||
| ALT-1 | PR0_ECAP0_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | AUDIO_EXT_REFCLK0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_UART0_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | EHRPWM1_B | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_10 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP0_I | ||||||||||||
| J2.70 | AP | Audio_WCLK | S | O | MCASP0_AFSX | SoC | D20 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MCASP0_AFSX | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI2_CS3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | AUDIO_EXT_REFCLK1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_12 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP1_B | ||||||||||||
| J2.72 | AP | Audio_DIN | S | I | MCASP0_AXR2 | SoC | A19 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MCASP0_AXR2 | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI2_D1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART1_RTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART6_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_IEP0_EDIO_DATA_IN_OUT29 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | ECAP2_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_UART0_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_8 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP0_B | ||||||||||||
| J2.74 | VAR | VAR_B_74 | S | O | I2C0_SCL | SoC | B16 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | Internal Internal 4K7 pull-upll-up, CMOS | ALT-0 | I2C0_SCL | |
| ALT-1 | PR0_IEP0_EDIO_DATA_IN_OUT30 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | SYNC0_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | OBSCLK0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART1_DCDn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | EQEP2_A | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | EHRPWM_SOCA | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_26 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | ECAP1_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-9 | SPI2_CS0 | ||||||||||||
| J2.76 | VAR | VAR_B_76 | S | IO | I2C0_SDA | SoC | A16 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | Internal Internal 4K7 pull-upll-up, CMOS | ALT-0 | I2C0_SDA | |
| ALT-1 | PR0_IEP0_EDIO_DATA_IN_OUT31 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | SPI2_CS2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | TIMER_IO5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART1_DSRn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | EQEP2_B | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | EHRPWM_SOCB | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_27 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | ECAP2_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| J2.78 | VAR | VAR_B_78 | OD | IO | ETH_INT | LAN | 39 | VDD_3V3 | Internal 4K7 pull-up | ||||
| J2.78 | VAR | VAR_B_78 (*) | OD | IO | ETH_INT | SoC | AB24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | Hardware mounting option (*) | ALT-0 | VOUT0_HSYNC | |
| ALT-1 | GPMC0_A16 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPO15 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPI15 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART3_RTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPO6 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_PRU0_GPI6 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_61 | ||||||||||||
| J2.80 | VAR | VAR_B_80 | OD | O | ETH_RST# | LAN | 43 | VDD_RGMII | Internal 10K pull-up | ||||
| J2.80 | VAR | VAR_B_80 (*) | OD | O | ETH_RST# | SoC | AA24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | Hardware mounting option (*) | ALT-0 | VOUT0_DATA13 | |
| ALT-1 | GPMC0_A13 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPO12 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPI12 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | UART5_CTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPO3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_PRU0_GPI3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_58 | ||||||||||||
| J2.82 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.84 | VAR | VAR_DIF_B_84 | D | WKUP_CLKOUT0 | SoC | A12 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | Hardware mounting option (*) | WKUP_CLKOUT0 | |||
| J2.86 | VAR | VAR_DIF_B_86 | D | EXT_REFCLK1 | SoC | A18 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | Hardware mounting option (*) | ALT-0 | SYNC1_OUT | ||
| ALT-2 | SPI2_CS3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | SYSCLKOUT0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | TIMER_IO4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | CLKOUT0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | CP_GEMAC_CPTS0_RFT_CLK | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_30 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | ECAP0_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| J2.88 | VAR | VAR_B_88 | OD | I | EXTINT# | SoC | D16 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | EXTINTn | ||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_31 | ||||||||||||
| J2.90 | VAR | VAR_DIF_B_90 | D | IO | GPMC0_AD02 | SoC | N24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE02 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD2 | |
| ALT-1 | PR0_PRU1_GPO10 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPI10 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR6 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_17 | ||||||||||||
| J2.92 | VAR | VAR_DIF_B_92 | D | IO | MCU_RESETZ | SoC | E11 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | MCU_RESETz | |||
| J2.94 | VAR | VAR_DIF_B_94 | D | IO | MCU_RESETSTATZ | SoC | B12 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | ALT-0 | MCU_RESETSTATz | ||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_21 | ||||||||||||
| J2.96 | VAR | VAR_DIF_B_96 | D | IO | MCU_ERROR# | SoC | D1 | VDD_1V8 | VDDS_OSC0 | 1.8 V | MCU_ERRORn | ||
| J2.98 | VAR | VAR_DIF_B_98 | D | IO | MCASP0_AXR3 | SoC | B19 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV0 | ALT-0 | MCASP0_AXR3 | ||
| ALT-1 | SPI2_D0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | UART1_CTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | UART6_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_IEP0_EDIO_DATA_IN_OUT28 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | ECAP1_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_UART0_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_7 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP0_A | ||||||||||||
| J2.100 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.102 | AP | CSI_CLK_N | D | I | CSI0_RXCLK_N | SoC | AD15 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_CSIRX | CSI0_RXCLK_N | |||
| J2.104 | AP | CSI_CLK_P | D | I | CSI0_RXCLK_P | SoC | AE15 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_CSIRX | CSI0_RXCLK_P | |||
| J2.106 | AP | CSI_D0_N | D | I | CSI0_RX0_N | SoC | AB14 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_CSIRX | CSI0_RX0_N | |||
| J2.108 | AP | CSI_D0_P | D | I | CSI0_RX0_P | SoC | AC15 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_CSIRX | CSI0_RX0_P | |||
| J2.110 | AP | CSI_D1_N | D | I | CSI0_RX1_N | SoC | AD14 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_CSIRX | CSI0_RX1_N | |||
| J2.112 | AP | CSI_D1_P | D | I | CSI0_RX1_P | SoC | AE14 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_CSIRX | CSI0_RX1_P | |||
| J2.114 | VAR | VAR_DIF_C_114 | D | I | CSI0_RX2_N | SoC | AD13 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_CSIRX | CSI0_RX2_N | |||
| J2.116 | VAR | VAR_DIF_C_116 | D | I | CSI0_RX2_P | SoC | AE13 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_CSIRX | CSI0_RX2_P | |||
| J2.118 | VAR | VAR_DIF_C_118 | D | I | CSI0_RX3_N | SoC | AB12 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_CSIRX | CSI0_RX3_N | |||
| J2.120 | VAR | VAR_DIF_C_120 | D | I | CSI0_RX3_P | SoC | AC13 | VDD_1V8 | VDDA_1P8_CSIRX | CSI0_RX3_P | |||
| J2.122 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.124 | VAR | VAR_C_124 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD05 | SoC | P22 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE05 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD5 | |
| ALT-1 | PR0_PRU1_GPO13 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPI13 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR9 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_20 | ||||||||||||
| J2.126 | VAR | VAR_C_126 | S | IO | GPMC0_AD06 | SoC | P21 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | BOOTMODE06 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_AD6 | |
| ALT-1 | PR0_PRU1_GPO14 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | PR0_PRU1_GPI14 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCASP2_AXR10 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO6 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI6 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_21 | ||||||||||||
| J2.128 | VAR | VAR_C_128 | OD | IO | WKUP_I2C0_SCL | SoC | B9 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | Internal 4K7 pull-up | ALT-0 | WKUP_I2C0_SCL | |
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_19 | ||||||||||||
| J2.130 | VAR | VAR_C_130 | OD | IO | WKUP_I2C0_SDA | SoC | A9 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | Internal 4K7 pull-up | ALT-0 | WKUP_I2C0_SDA | |
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_20 | ||||||||||||
| J2.132 | VAR | VAR_C_132 | S | IO | MCU_MCAN1_TX | SoC | E5 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | MCU_MCAN1_TX | ||
| ALT-1 | MCU_TIMER_IO2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCU_SPI1_CS1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | MCU_EXT_REFCLK0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_15 | ||||||||||||
| J2.134 | VAR | VAR_C_134 | S | IO | MCU_MCAN1_RX | SoC | D4 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | MCU_MCAN1_RX | ||
| ALT-1 | MCU_TIMER_IO3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCU_SPI0_CS2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCU_SPI1_CS2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | MCU_SPI1_CLK | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_16 | ||||||||||||
| J2.136 | VAR | S | IO | MCU_SPI0_CLK | SoC | A7 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | ALT-0 | MCU_SPI0_CLK | |||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_2 | ||||||||||||
| J2.138 | VAR | VAR_C_138 | S | IO | MCU_SPI0_CS0 | SoC | E8 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | ALT-0 | MCU_SPI0_CS0 | ||
| ALT-4 | WKUP_TIMER_IO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_0 | ||||||||||||
| J2.140 | VAR | VAR_C_140 | S | IO | MCU_SPI0_CS1 | SoC | B8 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | ALT-0 | MCU_SPI0_CS1 | ||
| ALT-1 | MCU_OBSCLK0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCU_SYSCLKOUT0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCU_EXT_REFCLK0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | MCU_TIMER_IO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | MCU_GPIO0_1 | ||||||||||||
| J2.142 | VAR | VAR_C_142 | S | IO | MCU_SPI0_D0 | SoC | D9 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | ALT-0 | MCU_SPI0_D0 | ||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_3 | ||||||||||||
| J2.144 | VAR | VAR_C_144 | S | IO | MCU_SPI0_D1 | SoC | C9 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_MCU | ALT-0 | MCU_SPI0_D1 | ||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_4 | ||||||||||||
| J2.146 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.148 | VAR | VAR_C_148 | S | IO | WKUP_UART0_RTS# | SoC | A4 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | WKUP_UART0_RTSn | ||
| ALT-1 | WKUP_TIMER_IO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCU_SPI1_CLK | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_12 | ||||||||||||
| J2.150 | VAR | VAR_C_150 | S | IO | WKUP_UART0_CTS# | SoC | C6 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | WKUP_UART0_CTSn | ||
| ALT-1 | WKUP_TIMER_IO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCU_SPI1_CS0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_11 | ||||||||||||
| J2.152 | VAR | VAR_C_152 | S | IO | MCU_UART0_CTS# | SoC | A6 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | MCU_UART0_CTSn | ||
| ALT-1 | MCU_TIMER_IO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCU_SPI1_D0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_7 | ||||||||||||
| J2.154 | VAR | VAR_C_154 | S | IO | MCU_UART0_RTS# | SoC | B6 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV_CANUART | ALT-0 | MCU_UART0_RTSn | ||
| ALT-1 | MCU_TIMER_IO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | MCU_SPI1_D1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | MCU_GPIO0_8 | ||||||||||||
| J2.156 | VAR | VAR_D_156 | S | IO | RGMII2_TD3 | SoC | AC20 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_TD3 | ||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_ACLKX | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPO16 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU1_GPI16 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_ECAP0_SYNC_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | PR0_UART0_CTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP2_S | ||||||||||||
| J2.158 | VAR | VAR_D_158 | S | IO | RGMII2_TD2 | SoC | AD21 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_TD2 | ||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_AFSX | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPO4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU1_GPI4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_ECAP0_IN_APWM_OUT | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_91 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP2_I | ||||||||||||
| J2.160 | VAR | VAR_D_160 | S | IO | RGMII2_TD1 | SoC | AA18 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_TD1 | ||
| ALT-1 | RMII2_TXD1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_ACLKR | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPO3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU1_GPI3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | MCASP2_AXR8 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_90 | ||||||||||||
| J2.162 | VAR | VAR_D_162 | S | IO | RGMII2_TD0 | SoC | Y18 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_TD0 | ||
| ALT-1 | RMII2_TXD0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_AXR6 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPO2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU1_GPI2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_89 | ||||||||||||
| J2.164 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.166 | VAR | VAR_D_166 | S | IO | RGMII2_TXC | SoC | AE21 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_TXC | ||
| ALT-1 | RMII2_CRS_DV | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_AXR5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU1_GPI1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_88 | ||||||||||||
| J2.168 | VAR | VAR_D_168 | S | IO | RGMII2_TX_CTL | SoC | AA19 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_TX_CTL | ||
| ALT-1 | RMII2_TX_EN | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_AXR4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU1_GPO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU1_GPI0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_87 | ||||||||||||
| J2.170 | VAR | VAR_D_170 | S | IO | MDIO0_MDC | SoC | AD24 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | MDIO0_MDC | ||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_86 | ||||||||||||
| J2.172 | VAR | VAR_D_172 | S | IO | MDIO0_MDIO | SoC | AB22 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | MDIO0_MDIO | ||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_85 | ||||||||||||
| J2.174 | VAR | VAR_D_174 | S | IO | RGMII2_RX_CTL | SoC | AD22 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_RX_CTL | ||
| ALT-1 | RMII2_RX_ER | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_AXR3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU0_GPO0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPI0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_1 | ||||||||||||
| J2.176 | VAR | VAR_D_176 | S | IO | RGMII2_RD0 | SoC | AE23 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_RD0 | ||
| ALT-1 | RMII2_RXD0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_AXR2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU0_GPO2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPI2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_UART0_RTSn | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_3 | ||||||||||||
| J2.178 | VAR | VAR_D_178 | S | IO | RGMII2_RD1 | SoC | AB20 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_RD1 | ||
| ALT-1 | RMII2_RXD1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_AFSR | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU0_GPO3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPI3 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | MCASP2_AXR7 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_4 | ||||||||||||
| J2.180 | VAR | VAR_D_180 | S | IO | RGMII2_RD2 | SoC | AC21 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_RD2 | ||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_AXR0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU0_GPO4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPI4 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_UART0_RXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_5 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP2_A | ||||||||||||
| J2.182 | VAR | VAR_D_182 | S | IO | RGMII2_RD3 | SoC | AE22 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_RD3 | ||
| ALT-2 | AUDIO_EXT_REFCLK0 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU0_GPO16 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPI16 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_UART0_TXD | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_6 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-8 | EQEP2_B | ||||||||||||
| J2.184 | VAR | VAR_D_184 | S | IO | RGMII2_RXC | SoC | AD23 | VDD_RGMII | VDDSHV2 | ALT-0 | RGMII2_RXC | ||
| ALT-1 | RMII2_REF_CLK | ||||||||||||
| ALT-2 | MCASP2_AXR1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-3 | PR0_PRU0_GPO1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPI1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_ECAP0_SYNC_IN | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO1_2 | ||||||||||||
| J2.186 | AP | USB_A_VBUS | A | I | USB0_VBUS | SoC | AC11 | VDD_3V3 | VDDA_3P3_USB | Buffered, Vth = 3,54 V | |||
| J2.188 | AP | USB_B_VBUS | A | I | USB1_VBUS | SoC | AB10 | VDD_3V3 | VDDA_3P3_USB | Buffered, Vth = 3,54 V | |||
| J2.190 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
| J2.192 | AP | USB_A_ID | S | IO | GPMC0_ADV_ALE# | SoC | L23 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_ADV_ALE# | ||
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_AXR2 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO9 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI9 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA7 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_32 | ||||||||||||
| J2.194 | AP | USB_B_ID | S | IO | GPMC0_OE_RE# | SoC | L24 | VDD_3V3 | VDDSHV3 | ALT-0 | GPMC0_OE_RE# | ||
| ALT-2 | MCASP1_AXR1 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-4 | PR0_PRU0_GPO10 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-5 | PR0_PRU0_GPI10 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-6 | TRC_DATA8 | ||||||||||||
| ALT-7 | GPIO0_33 | ||||||||||||
| J2.196 | AP | USB_A_N | D | IO | USB0_D_N | SoC | AE11 | VDD_3V3 | VDDA_3P3_USB | ||||
| J2.198 | AP | USB_A_P | D | IO | USB0_D_P | SoC | AD11 | VDD_3V3 | VDDA_3P3_USB | ||||
| J2.200 | AP | USB_B_N | D | IO | USB1_D_N | SoC | AD10 | VDD_3V3 | VDDA_3P3_USB | ||||
| J2.202 | AP | USB_B_P | D | IO | USB1_D_P | SoC | AE9 | VDD_3V3 | VDDA_3P3_USB | ||||
| J2.204 | AP | DGND | G | DGND | |||||||||
Power and reset[edit | edit source]
Power Supply Unit (PSU) and recommended power-up sequence[edit | edit source]
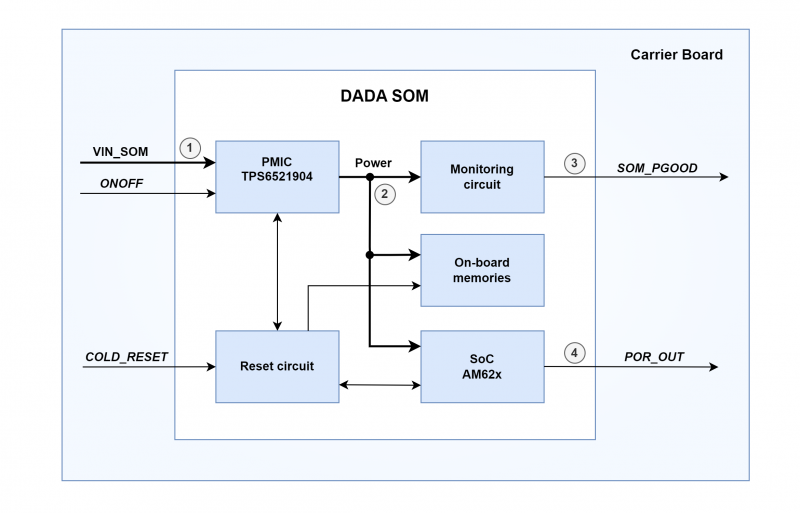
Implementing correct power-up sequence for AM62x SoC processors is not a trivial task because several power rails are involved.
DADA SOM simplifies this task by embedding all the needed circuitry. The following picture shows a simplified block diagram of PSU/voltage monitoring circuitry:
The PSU is composed of two main blocks:
- power management integrated circuit (PMIC)
- additional generic power management circuitry that completes PMIC functionalities
The PSU:
- generates the proper power-up sequence required by the SoC processor and surrounding memories and peripherals
- synchronizes the powering up of carrier board's circuitry to prevent back powering
See the pinout section for more details on the signals.
Power-up sequence[edit | edit source]
The typical power-up sequence is the following:
- VIN_SOM (+3.3V) main power supply rail is powered.
- POR_OUT (active-low) is driven low; PMIC initiates power-up sequence needed by AM62x processor.
- SOM_PGOOD goes up when all SoC, memories, and I/O power rails are ready.
- Finally, the processor is brought out of reset and the POR_OUT signal is released.
For a detailed description of the reset circuit and its signals see the page Reset_scheme_and_control_signals.
Control signals and their purpose[edit | edit source]
SOM_PGOOD[edit | edit source]
SOM_PGOOD is generally used on carrier board to drive loads such as DC/DC enable inputs or switch on/off control signals in order to prevent back power.
Depending on the kind of such loads, SOM_PGOOD might not be able to drive them properly. On DADA SoM this signal is driven by a push-pull output at VIN_SOM (3.3 V) rail, with max 10 mA output current (recommended 1 mA).
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a always-present type signal i.e. the pin only covers this functionality on any other Industrial SoM.
ONOFF[edit | edit source]
Long ONOFF signal retention causes the SoM to turn OFF or ON, with a complete power off/on sequence. This is not intended as a low-power mode, since completely turning off the SoM causes the loss of volatile content such as data in RAM.
When the SoM is first powered it turns on without acting on ONOFF signal.
On SoM the signal is pulled-up with 10 kOhm to VIN_SOM (3.3 V).
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a variable type signal i.e. the pin can assume different functions on other Industrial SoMs.
COLD_RESET[edit | edit source]
COLD_RESET is an input signal that cause a SoC cold reset. On SoM the signal is pulled-up with 10 kOhm to VDD_3V3 (3.3 V).
A cold reset of the SoC does not result in a complete power sequence of the SoM.
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a always-present type signal i.e. the pin only covers this functionality on any other Industrial SoM.
POR_OUT[edit | edit source]
POR_OUT is an open-drain output (a pull-up on a carrier is required) to be used to reset peripherals on carriers. The signal is released by the SoC when it exits reset (either cold or warm reset).
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a variable type signal i.e. the pin can assume different functions on other Industrial SoMs.
Note on reset signals usage and carrier board PSU[edit | edit source]
In Unica Industrial Dave standard, only SOM_PGOOD and COLD_RESET signals were foreseen as always-present. With only the SOM_PGOOD output signal you need to:
- ensure the carrier PSU activates before the SoM exits reset (for DADA SoM POR_OUT is released about 17 ms after SOM_PGOOD)
- generate a peripheral reset signal on the carrier
It is possible if variable signals are also available:
- with POR_OUT output: reset the peripherals on carrier synchronously with the SoM
- with WARM_RESET input: keep SoM in reset until the carrier PSU is active
Reset scheme and control signals[edit | edit source]
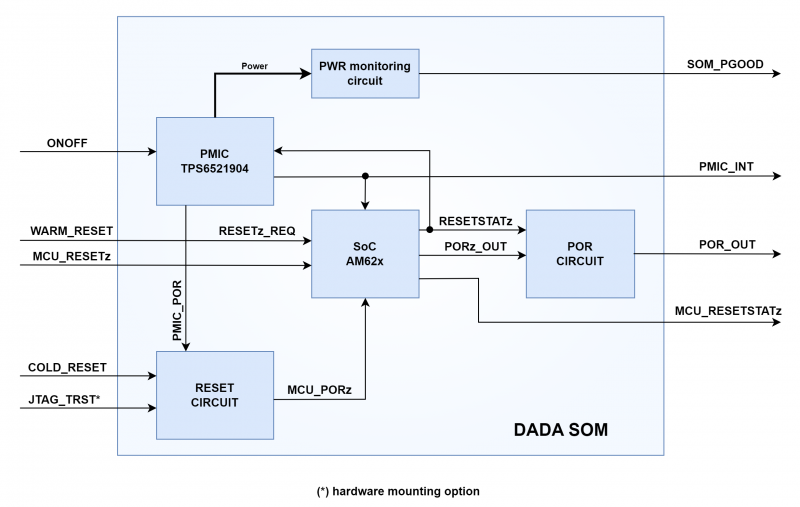
The AM62x SoC provides several reset signals for its different domains: the following table summarises the TI nomenclature and purpose. Reading "AM62x Processors Technical Reference Manual" [1] is highly recommended.
| SoC signal | SoC domain | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCU_PORz | MCU | Input | MCU Domain cold reset |
| MCU_RESETz | MCU | Input | MCU Domain warm reset |
| RESETz_REQ | Main | Input | Main Domain external warm reset request |
| PORz_OUT | Main | Output | Main Domain POR status output |
| MCU_RESETSTATz | MCU | Output | MCU Domain warm reset status output |
| RESETSTATz | Main | Output | Main Domain warm reset status output |
The following picture instead shows the simplified block diagram of reset scheme and voltage monitoring, referring to the nomenclature of the DADA signals.
The six reset signals of SoC are all usable by the SoM. When designing the SoM pinout, the MCU domain signals were mapped separately, while the Main domain signals were mapped to functions defined in Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout.
See the pinout section for more details on the signals.
Reset signals and their purpose[edit | edit source]
COLD_RESET[edit | edit source]
COLD_RESET is an input signal that cause a SoC cold reset. On SoM the signal is pulled-up with 10 kOhm to VDD_3V3 (3.3 V).
A cold reset of the SoC does not result in a complete power sequence of the SoM.
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a always-present type signal i.e. the pin only covers this functionality on any other Industrial SoM.
WARM_RESET[edit | edit source]
WARM_RESET is connected to RESETz_REQ SoC input that starts the main domain warm reset. On SoM the signal is pulled-up with 10 kOhm to VDD_3V3 (3.3 V).
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a variable type signal i.e. the pin can assume different functions on other Industrial SoMs.
MCU_RESETz[edit | edit source]
MCU_RESETz is a SoC input (VDD_3V3) that starts the MCU domain warm reset.
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a variable type signal i.e. the pin can assume different functions on other Industrial SoMs.
POR_OUT[edit | edit source]
POR_OUT is an open-drain output (a pull-up on a carrier is required) to be used to reset peripherals on carriers. The signal is released by the SoC when it exits reset (either cold or warm main domain reset).
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a variable type signal i.e. the pin can assume different functions on other Industrial SoMs.
MCU_RESETSTATz[edit | edit source]
MCU_RESETSTATz is a push-pull (VDD_3V3) SoC output, released by the SoC when it MCU domain exits warm reset.
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a variable type signal i.e. the pin can assume different functions on other Industrial SoMs.
PMIC_INT[edit | edit source]
PMIC_INT is a open-drain PMIC output; on SoM the signal is pulled-up with 10 kOhm to VDD_3V3 (3.3 V).
The signal is asserted low in case of PMIC fault condition.
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a always-present type signal i.e. the pin only covers this functionality on any other Industrial SoM.
ONOFF[edit | edit source]
Long ONOFF signal retention causes the SoM to turn OFF or ON, with a complete power off/on sequence. This is not intended as a low-power mode, since completely turning off the SoM causes the loss of volatile content such as data in RAM. When the SoM is first powered it turns on without acting on ONOFF signal.
On SoM the signal is pulled-up with 10 kOhm to VIN_SOM (3.3 V).
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a variable type signal i.e. the pin can assume different functions on other Industrial SoMs.
SOM_PGOOD[edit | edit source]
SOM_PGOOD is generally used on carrier board to drive loads such as DC/DC enable inputs or switch on/off control signals in order to prevent back power.
Depending on the kind of such loads, SOM_PGOOD might not be able to drive them properly. On DADA SoM this signal is driven by a push-pull output at VIN_SOM (3.3 V) rail, with max 10 mA output current (recommended 1 mA).
On Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout it is a always-present type signal i.e. the pin only covers this functionality on any other Industrial SoM.
JTAG_TRST[edit | edit source]
This signal is connected to the JTAG cell (see JTAG page). With a hardware variant, it is also possible to force a cold reset of the SoC with this signal.
References[edit | edit source]
[1] TI, AM62x Processors Silicon Revision 1.0, Technical Reference Manual
System boot[edit | edit source]
|
This page illustrates the characteristics of the DADA's boot subsystem. Reading of the chapter Initialization of the "AM62x Processors Technical Reference Manual" [1] is highly recommended, though. AM62x SoC features several options in terms of booting. Such options are detailed in that document. |
The boot process begins at Power On Reset (POR) where the hardware reset logic forces the ARM core to begin execution starting from the on-chip boot ROM. The boot ROM:
- determines whether the boot is secure or non-secure
- performs some initialization of the system and clean-ups
- reads the mode pins to determine the primary boot device
- once it is satisfied, it executes the boot code
Boot options[edit | edit source]
The default primary boot device is defined at the factory and identified by the 'Boot Mode' field of the ordering code as follows:
- 0: on board QSPI NOR or MMC1 (uSD) option (SoM code: DSAAxxx0xxxxR)
- 1: on board eMMC or MMC1 (uSD) option (SoM code: DSAAxxx1xxxxR)
For both options an alternative primary boot from SD/MMC card is provided, selectable by driving low the BOOT_MODE_SEL signal: BOOT_MODE_SEL is latched when processor reset is released.
Bootable SD/MMC card connects via the MMC1 bus, mapped on SDIO_A bus referring to Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout.
If primary boot fails, the bootrom goes to the 'USB boot mode' to read the boot image from external USB host, connected to the USB0 bus.
| Ordering code 'Boot Mode' fileld | BOOT_MODE_SEL | Primary boot mode/device | Backup boot mode/device |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | SD/MMC card on MMC1 bus | USB host on USB0 bus |
| 1 | QSPI NOR on OSPI0 bus | ||
| 1 | 0 | SD/MMC card on MMC1 bus | USB host on USB0 bus |
| 1 | eMMC on MMC0 bus |
Other options are available on-demand, however, allowing the implementation of different configurations. DAVE Embedded Systems' team is available for additional information on this matter, please contact sales@dave.eu.
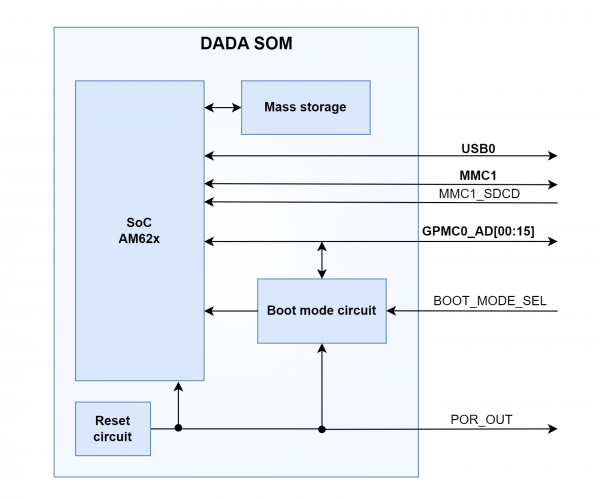
Note on boot signals[edit | edit source]
Bootstrap stage has to be intended as the time elapsing between the release of hardware reset (POR_OUT) and the execution of the first instruction of user code (typically this is the reset vector of U-Boot boot loader). The following figure shows the signals involved in the boot phase.
See the pinout section for more details on the signals.
The following boot signals are latched by the 'boot mode circuit' when processor reset POR_OUT signal is released.
BOOT_MODE_SEL[edit | edit source]
Inside the SOM, BOOT_MODE_SEL signal is pulled-up with 10 kohm.
SD card detect[edit | edit source]
Boot ROM detects SD/MMC card on MMC1 bus: if a card is inserted, ROM will try to boot from it.
MMC1_SDCD signal (named SDIO_A_CD on Unica Industrial Dave standard pinout) is used as card detect signal during bootstrap stage: this signal need to be kept low for boot from SD/MMC card.
Inside the SOM, MMC1_SDCD signal is pulled-up with 10 kohm.
Bootstrap bits[edit | edit source]
Upon exiting the reset the 'boot mode circuit' samples the value of the bootstrap bits, belonging to the GPMC0_AD[0:15] lines:
- to set these bits there are PULL-UP or PULL-DOWN resistors on SoM
- all signals are routed to SoM J1 connector interface, so they can be externally modified by forcing a voltage values
When developing the carrier board, pay attention to the connection of these signals (they have a PD or PU resistance, avoid applying voltages during bootstrap stage).
References[edit | edit source]
[1] TI, AM62x Processors Silicon Revision 1.0, Technical Reference Manual
JTAG[edit | edit source]
JTAG signals are routed to the J1 primary connector of the DADA PCB. These signals output at 3.3 V logic.
For standard operation, the JTAG cell remains in reset: this is ensured by an on SoM pull-down resistor on JTAG_TRSTn signal. To enable a JTAG interface, drive the JTAG_TRSTn signal high.
| Pin | Pin type | UNICA pin name | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| J1.56 | Always present | DGND | - |
| J1.52 | Always present | JTAG_TCK | Input CMOS 3.3 V |
| J1.50 | Always present | JTAG_TMS | Input CMOS 3.3 V |
| J1.54 | Always present | JTAG_TDO | Ouput CMOS 3.3 V |
| J1.48 | Always present | JTAG_TDI | Input CMOS 3.3 V |
| J1.46 | Variable | JTAG_TRSTn | Input CMOS 3.3 V with 10K pull-down. |
See the pinout section for more details.
For additional features such as boundary scan, please contact DAVE Embedded Systems' team sales@dave.eu.
Peripherals[edit | edit source]
Peripheral Ethernet[edit | edit source]
The DADA SOM has a 3-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW0) subsystem that provides Ethernet packet communication for the device and can be configured as an Ethernet switch.
Description[edit | edit source]
The 3-port CPSW0 subsystem provides the following features:
- Two Ethernet ports (port 1 and 2) with selectable RGMII and RMII interfaces and an internal Communications Port Programming Interface (CPPI) port (port 0)
- Synchronous 10/100/1000 Mbit operation: full duplex mode supported in 10/100/1000 Mbps. Half-duplex mode supported only in 10/100 Mbps modes only
- Flexible logical FIFO-based packet buffer structure
- Eight priority level Quality Of Service (QOS) support (802.1p)
- Support for Audio/Video Bridging (P802.1Qav/D6.0)
- Support for IEEE 1588 Clock Synchronization (2008 Annex D, Annex E and Annex F)
- Timestamp module capable of time stamping external timesync events like Pulse-Per-Second and also generating Pulse-Per-Second outputs
- CPTS module that supports time stamping for IEEE1588 with support for 4 hardware push events and generation of compare output pulses
- Maximum frame size of 2024 bytes
- Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) module for PHY Management with Clause 45 support
- DSCP Priority Mapping (IPv4 and IPv6)
- Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) support (802.3az)
- Flow Control Support (802.3x)
- Wire rate switching (802.1d)
- Non-Blocking switch fabric
- Time Sensitive Network Support (IEEE P802.3br Interspersing Express Traffic, IEEE 802.1Qbv Enhancements for Scheduled Traffic)
- Address Lookup Engine (ALE with configurable number of addresses plus VLANs, spanning tree support, MAC authentication 802.1x and blocking, OUI (Vendor ID) host accept/deny feature, VLAN support)
- 802.1Q compliant (Auto add port VLAN for untagged frames on ingress and Auto VLAN removal on egress and auto pad to minimum frame size)
- EtherStats and 802.3Stats Remote Network Monitoring (RMON) statistics gathering (per port statistics)
- Ethernet Mac transmit to Ethernet Mac receive Loopback mode (digital loopback) supported
Peripheral MMC[edit | edit source]
Each MMCSD instance - in the DADA SOM - includes one MMCSD Host Controller. A host controller can support eMMC and/or SD/SDIO. Up to 2 (two) MMCSD ports are available in the DADA SOM.
Description[edit | edit source]
- Each MMCSD module has the following features:
- Advanced DMA
- System Bus Interface:
- 64-bit data width (host interface)
- 64-bit address
- Clock asynchronous to MMCSD clock (MMCi_CLK)
- Configuration Bus Interface:
- 32-bit data width (target interface)
- Linear incrementing addressing mode
- 32-bit aligned accesses only
- MMCSD Host Controller - eMMC interface (see the device-specific AM62x datasheet for supported instances):
- Multi-Media Card Support
- eMMC Electrical Standard 5.1 (JESD84-B51)
- Backward compatible with earlier eMMC standards
- Legacy MMC SDR
- High Speed SDR
- High Speed DDR
- HS200 SDR
- Multi-Media Card Support
- MMCSD Host Controller - SD/SDIO interface (see the device-specific AM62x datasheet for supported instances):
- Secure Digital Card Support
- Backward compatible with earlier SD card specifications
- SD Host Controller Standard Specification 4.10 and SD Physical Layer Specification v3.01, SDIO Specification v3.00
- Default Speed mode
- High Speed mode
- SDR12, SDR25, SDR50, DDR50 (UHS-I 1.8 V)
- Secure Digital Card Support
Peripheral USB[edit | edit source]
The AM62x SoC instantiates two independent instances of a third-party USB subsystem (USB2SS) operating at up to USB2.0 speeds (480Mb/s), either of which can be independently configured to act as a USB Host or a USB Device.
Description[edit | edit source]
The USB 2.0 subsystem (USB2SS) supports the following USB Features:
- Operational modes:
- Supports USB 2.0 Host mode at High-Speed (HS, 480 Mbps), Full-Speed (FS, 12 Mbps), and Low-Speed (LS, 1.5 Mbps)
- Supports USB 2.0 Device mode at High-Speed (HS, 480 Mbps), and Full-Speed (FS, 12 Mbps). Low-Speed is not supported in Device mode
- Supports all modes of transfers - Control, Bulk, Interrupt, and Isochronous
- A DRD (Dual-Role-Device - Host or Device) USB controller with the following features:
- Compatible to the xHCI 1.0 specification in Host mode
- Compatible with the USB 2.0 specification in Device mode
- Supports 15 IN (Receive), 15 OUT (Transmit) endpoints (EPs), and one EP0 endpoint which is bidirectional
- Operation flexibility
- Same programming model for HS, FS, and LS operation
- Each controller instance can provide either USB Host or USB Device functionality
Peripheral Display Subsystem[edit | edit source]
The Display Subsystem (DSS) - in the DADA SOM - is a flexible, multi-pipeline subsystem that supports high-resolution display outputs. Display outputs can connect seamlessly to an Open LVDS Display Interface transmitter (OLDITX), or can directly drive device pads as a Display Parallel Interface (DPI).
Description[edit | edit source]
The Display Subsystem module includes the following features:
- Two display outputs
- up to 24-bit per pixel parallel or embedded sync output
- up to 200MHz pizel clock
- supports
- 1920x1080@60 fps
- 1x 2048x1080 + 1x 1280x720
- RGB/YUV422 modes
- Progressive/interlaced modes
- two display pipelines support 2x Open LVDS Interface 4-data/1clk link (either shared to provide a 4K display or mirroring the same display - independent displays on each OLDI are not supported)
- Two input display processing pipelines
- one video pipeline supporting full RGB and 8/10-bit YUV data formats capable of 0.25x to 16x resizing
- one video_lite pipeline supporting full RGB and 8/10 YUV data formats (no resizing support)
- Two Overlay Managers with multi-layer alpha blending
- One DMA controller capable of supporting up to 2K input source width
- On-the-fly X/Y-axis Flip/Mirror mode support
Peripheral Camera Subsystem[edit | edit source]
The Camera Serial Interface Receiver (CSI_RX_IF) - in the DADA SOM - allows the device to stream video inputs from multiple cameras to internal memory.
Description[edit | edit source]
The CSI_RX_IF module supports the following features:
- Compliant to MIPI CSI v1.3
- supports up to 16 virtual channels per input (partial MIPI CSI v2.0 feature)
- Data rate up to 2.5 Gbps per lane (wire rate)
- Supports 1, 2, 3, or 4 Data Lane connection to DPHY_RX
- Programmable formats including YUV420, YUV422, RGB, Raw, and User Defined (over 25 different formats supported)
- One independent (simultaneous) output stream:
- One (up to 32 Channels) DMA interface through a 128-bit PSI_L connection to DMSS for transfers to memory:
- Byte packed (32x4) format, elastic buffer mode, max rate 1 data cycle every 4 main clocks
- 32 thread ID’s supported (virtual channel & data type combinations); Flexible number of threads (32 Max)
- Virtual channels and data types mapped via mmr to PSI_L thread ID’s
- Internal FF based FIFO; RAM based buffer (2kx128)
- One (up to 32 Channels) DMA interface through a 128-bit PSI_L connection to DMSS for transfers to memory:
- Video inputs come from the DPHY_RX which allows the camera physical port module to grab video streams from external sensor cameras and other CSI2 compliant sources
- Compliant to MIPI D-PHY standard v1.2
- Supports up to 4 data and 1 clock lanes
- Supports up to 2.5 Gbps (with deskew) and 1.5 Gbps (without deskew) per data lane
Peripheral Industrial interfaces[edit | edit source]
The AM62x SoC in the DADA SOM has several industrial interfaces for automotive and industrial applications like Industrial HMI, driver monitoring systems, EV charging stations.
Description[edit | edit source]
The following industrial interfaces are available:
- 3x enhanced PWM modules (ePWM)
- 3x enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse modules (eQEP)
- 3x enhanced Capture modules (ECAP)
- Timer modules
Enhanced Pulse Width Modulation[edit | edit source]
The Enhanced Pulse Width Modulation (ePWM) interface (DSMIF) is able to generate complex pulse width waveforms with minimal CPU overhead or intervention.
The three ePWM modules support the following features:
- Dedicated 16-bit time-base counter with period and frequency control
- Two PWM outputs (EPWMxA and EPWMxB) that can be used as two independent PWM outputs with single-edge operation, two independent PWM outputs with dual-edge symmetric operation or one independent PWM output with dual-edge asymmetric operation
- Asynchronous override control of PWM signals through software
- Programmable phase-control support for lag or lead operation relative to other EPWM modules
- Hardware-locked (synchronized) phase relationship on a cycle-by-cycle basis
- Dead-band generation with independent rising and falling edge delay control
- Programmable trip zone allocation of both cycle-by-cycle trip and one-shot trip on fault conditions
- A trip condition can force either high, low, or high-impedance state logic levels at PWM outputs
- Allows events to trigger both CPU interrupts and ADC start of conversions
- PWM chopping by a high-frequency carrier signal, useful for pulse transformer gate drives
Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse modules[edit | edit source]
The Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (EQEP) peripheral is used for direct interface with a linear or rotary incremental encoder to get position, direction and speed information from a rotating machine for use in high performance motion and position control system.
The three eQEP include the following features:
- Input synchronization
- Three stage/six stage digital noise filter
- Quadrature decoder unit
- Position counter and control unit for position measurement
- Quadrature edge capture unit for low-speed measurement
- Unit time base for speed and frequency measurement
- Watchdog timer for detecting stalls
- EQEP inputs (A/B/INDEX and STROBE) are available at chip level
- EQEP phase error output is also available
Enhanced Capture modules[edit | edit source]
The Enhanced Capture (ECAP) module can be used for:
- Sample rate measurements of audio inputs
- Speed measurements of rotating machinery (for example, toothed sprockets sensed via Hall sensors)
- Elapsed time measurements between position sensor pulses
- Period and duty cycle measurements of pulse train signals
- Decoding current or voltage amplitude derived from duty cycle encoded current/voltage sensors
The ECAP module includes the following features:
- 32-bit time base counter
- 4 × 32 bits event time-stamp capture registers (ECAP0_CAP1 through ECAP0_CAP4)
- 4-stage sequencer (Mod4 counter), synchronized to external events (ECAPx pin edges)
- Independent edge polarity (rising/falling edge) selection for all 4 sequenced time-stamp capture events
- Input capture signal pre-scaling (from 1 to 16)
- One-shot compare register (2 bits) to freeze captures after 1 to 4 time-stamp events
- Continuous mode capture of time-stamps in a four-deep circular buffer
- Absolute time-stamp capture
- Difference (Delta) mode time-stamp capture
- When not used in capture mode, the ECAP module can be configured as a single-channel PWM output
Timer modules[edit | edit source]
One Industrial 64-bit timer with 9 capture and 16 compare events, along with slow and fast compensation, is available with the following features:
GTC[edit | edit source]
- The GTC module provides a continuous running counter that can be used for time synchronization and debug trace time stamping and supports the following features:
- 64-bit up counter (No rollover during the lifetime of the device)
- Compatible with ARMv8 system counter requirements:
- Disabled at power-up
- Register definition and memory map aligned to ARMv8 definition
- Implements memory-mapped counter control and status frames
- Outputs reflected binary (Gray) encoded timer value for system timer bus distribution to other modules
- Selectable counter bit output as a push event that can be used by CPTS modules, timers or interface protocols
Windowed Watchdog Timer (WWDT)[edit | edit source]
The Windowed Watchdog Timer (WWDT), implemented by using the Digital Windowed Watchdog (DWWD) function of the Real Time Interrupt (RTI) module in the device
The RTI modules include the following main features:
- Windowed Watchdog Timer (WWDT) feature
- Two independent 64 bit counter blocks (counter block0 or counter block1). Each block consists of one 32 bit up counter and one 32 bit free running counter
- Two capture registers for capturing the prescale and free running counter on a special event.
- Free running counter 0 can be incremented by either the internal prescale counter or by an external event
- Four configurable compare registers for generating operating system ticks . Each event can be driven by either counter block0 or counter block1
- RTI clock input derived from any of the available clock sources, selectable in the System Module
- Optional capability to drive a pulse-width modulated signal out on an interrupt line
Real Time Clock[edit | edit source]
The RTC is to keep time of day and the important purpose is for Digital Rights management. Tamper proofing is needed to ensure that simply stopping, resetting, or corrupting the RTC does not go unnoticed so that if this occurs, the application can re-acquire the time of day from a trusted source.
The real-time clock (RTC) provides the following features:
- With Analog IP block: 2 digital voltage domains with integrated LVL/ISO cells, RTC or Always ON domain
- Without Analog IP block: 1 digital voltage domain, no lvl.iso
- 15 bit 32768Hz counter
- 48 bit seconds counter with +/- 1 30uS upto +/- 1 S drift adjustment every 4048 Seconds
- 256 bits of Scratch PAD
- 1 ON_OFF compare event, 48-bits / 1 OFF_ON compare event, 48-bits / 2 event outputs OFF_ON and ON_OFF to CORE
- Support active external 32768 Hz and inactive/gated 32768 Hz
• Some of the counter registers as general purpose
- Functional lockout, unlock by special vbusp sequence, DFT lockout, unlock by special 1500 sequence
• HOST PROCESSOR can issue OFF now cmd, update MMRs without polling, thanks to HW Shadow/Auto Sync, read time without polling, thanks to HW Shadow/Auto Sync
- External IOs (Optional): 4 wakeup inputs with active high/low including optional debounce
- Async wake up supported: 1 pmic_enable output
Peripheral PRUSS[edit | edit source]
The PRU Subsystem (PRUSS) - in the AM62x SoC - is a subset of the PRU Industrial Communication Subsystem (PRU-ICSS) found on other TI processors.
The programmable nature of the PRU cores provides flexibility in implementing fast real-time responses, specialized data handling operations, custom peripheral interfaces, and in offloading tasks from the other processor cores of the device.
The PRU cores are programmed with a small, deterministic instruction set. Each PRU can operate independently or in coordination with each other and can also work in coordination with the device-level host CPU.
Description[edit | edit source]
The Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS) consists of:
- Two 32-bit load/store RISC CPU cores — Programmable Real-Time Units (PRU0 and PRU1)
- Data RAMs per PRU core (DRAM)
- Instruction RAMs per PRU core (IRAM)
- Shared RAM (SRAM)
- Peripheral modules: UART0, ECAP0, IEP0, MDIO
- Interrupt Controller (INTC) per core
The PRUSS subsystem includes the following main features:
- Two 32-bit load/store RISC CPU cores — Programmable Real-Time Units (PRU0 and PRU1), each with:
- 20 Enhanced General-Purpose Inputs (EGPI) and 20 Enhanced General-Purpose Outputs (EGPO)
- Asynchronous capture [Serial Capture Unit (SCU)] with 3-channel peripheral interface and Sigma-Delta demodulation support
- The 3-channel peripheral interface supports multiple different encoder protocols such as EnDAT 2.2, HDSL, and Tamagawa
- program memory per PRU (PRU0_IRAM and PRU1_IRAM) with ECC
- MAC (Multiplier with optional Accumulation)
- CRC16/CRC32 hardware accelerator
- RX XFR2VBUS
- Scratchpad Memory (SPAD) with 3 banks of 30 × 32-bit registers: 3 banks for the PRU0 and PRU1 cores
- 32 KB Shared general purpose memory RAM with ECC (Data RAM2), shared between PRU0 and PRU1
- Two 8 KB (shared) Data Memories with ECC (Data RAM0 and Data RAM1)
- 36-bit VBUSM Controller Port: optional address translation for all transactions to External Host
- 16 Software Events generated by 2 PRUs
- One Enhanced Capture Module (ECAP0)
- Interrupt Controller (INTC)
- Up to 32 internal events, generated by modules, internal to the PRUSS
- Up to 32 external events, generated by the system
- Supports up to 10 interrupt channels
- Generation of 8 Host interrupts:
- 8 Host interrupts, exported from the PRUSS for signaling the Arm interrupt controllers (pulse and level provided)
- Hardware prioritization of events
- Flexible power management support
- Integrated 32-bit Interconnect
Peripheral Audio[edit | edit source]
The Multichannel Audio Serial Port (MCASP) module - in the DADA SOM - supports time-division multiplexed (TDM) stream, Inter-IC Sound (I2S) protocols reception and transmission and an inter-component digital audio interface transmission (DIT).
Description[edit | edit source]
Each MCASP module has the following features:
- Independent serializer for each AXRx channel of each MCASP module
- Two independent clock generator modules for transmit and receive (receive and transmit at different clock rates).
- Functional clock can be generated:
- Internally (controller mode)
- Supplied over MCASP serial interface (target mode)
- controllable functional clock divide ratio
- Independent transmit and receive modules, each includes:
- Programmable clock and frame sync generator
- TDM streams from 2 to 32, and 384 time slots
- Support for time slot sizes of 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, and 32 bits
- bit manipulation
- Glueless connection to audio ADC, DAC, codec, digital audio interface receiver (DIR), and S/PDIF physical layer components
- Integrated digital audio interface transmitter (DIT):
- S/PDIF, IEC60958-1, AES-3 formats
- 384-slot TDM with external digital audio interface receiver (DIR) device: an external DIR receiver integrated circuit should be used with I2S output format
- Support for 2 × DMA requests (one per direction)
- One transmit and one receive interrupt request common for all serializers
Peripheral CAN[edit | edit source]
The MCAN modules in the DADA SOM conform to the CAN Protocol 2.0 A, B and ISO 11898-1. The MCAN module supports both classic CAN and CAN FD (CAN with Flexible Data-Rate) specifications. CAN FD feature allows high throughput and increased payload per data frame.
Description[edit | edit source]
Each MCAN module has the following features:
- Full CAN FD support (up to 64 data bytes)
- SAE J1939 support
- AUTOSAR support
- Up to 32 dedicated Transmit Buffers: configurable Transmit FIFO, Transmit Queue and Transmit Event FIFO up to 32 elements (each one)
- Up to 64 dedicated Receive Buffers: two configurable Receive FIFOs, up to 64 elements each
- Up to 128 filter elements
- Internal Loopback mode for self-test
- Two clock domains (CAN clock/Host clock)
- Parity/ECC support - Message RAM single error correction and double error detection (SECDED) mechanism
- Timestamp Counter
Peripheral SPI[edit | edit source]
The MCSPI module - in the DADA SOM - is a multichannel transmit/receive, controller/peripheral synchronous serial bus. Up to 5 (five) SPI ports are available in the DADA SOM.
Description[edit | edit source]
Each MCSPI module has the following features:
- Serial clock with programmable frequency, polarity, and phase for each channel
- Wide selection of MCSPI word lengths, ranging from 4 to 32 bits
- Up to four controller channels, or single channel in peripheral mode
- Controller multichannel mode:
- Full duplex/half duplex
- Transmit-only/receive-only/transmit-and-receive modes
- Flexible input/output (I/O) port controls per channel
- Programmable clock granularity
- MCSPI configuration per channel. This means, clock definition, polarity enabling and word width
- Enable the addition of a programmable start-bit for MCSPI transfer per channel (start-bit mode)
- Supports start-bit write command, pause and break sequence
- Programmable shift operations (1-32 bits)
- Programmable timing control between chip select and external clock generation
Peripheral I2C[edit | edit source]
The I2C modules in the DADA SOM are compliant with Philips I2C-bus specification version 2.1. Up to 6 (six) I2C ports are available in the DADA SOM.
Description[edit | edit source]
Each I2C module has the following features:
- Supports a standard mode (up to 100 Kbps) and fast mode (up to 400 Kbps)
- Supports HS mode (up to 3.4 Mbps) - only in 1.8 V mode
- 7-bit and 10-bit device addressing modes
- General call, Start/Restart/Stop
- Multicontroller transmitter/target receiver mode and receiver/target transmitter mode
- Combined controller transmit/receive and receive/transmit mode
- Built-in FIFO for buffered read
- Programmable multitarget channel (responds to four separate addresses)
- Low power consumption
- Support Auto Idle mechanism, Idle Request/Idle Acknowledge handshake mechanism and asynchronous wakeup mechanism
Peripheral UART[edit | edit source]
The Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) is a peripheral that utilizes the DMA for data transfer or interrupt polling via the host CPU. All UART modules support IrDA and CIR modes when 48 MHz function clock is used. Up to 9 (nine) UARTs are available in the DADA SOM.
Description[edit | edit source]
Each UART module has the following features:
- 16C750-compatible
- RS-485 external transceiver auto flow control support
- 64-byte FIFO buffer for receiver and 64-byte FIFO buffer for transmitter with programmable interrupt trigger levels for FIFOs
- The 48 MHz functional clock is default option and allows baud rates up to 3.6 Mbps
- Auto-baud between 1200 bits/s and 115.2 Kbits/s (only when 48 MHz function clock is used)
- Optional multi-drop transmission
- Configurable data format:
- Parity bit: Even, odd, none
- Stop-bit: 1, 1.5, 2 bit(s)
- Flow control: Hardware (RTS/CTS) or software (XON/XOFF) and modem control functions (CTS, RTS)
- Internal test and loopback capabilities
- UART0 module in MAIN domain has extended modem control signals (DCD, RI, DTR, DSR)
Peripheral GPIOs[edit | edit source]
The General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) peripheral provides dedicated general-purpose pins that can be configured as either inputs or outputs. The GPIO pins are grouped into banks (16 pins per bank and 9 banks per module), which means that each GPIO module provides up to 144 dedicated GPIO. Up to 432 GPIOs (3 modules x 9 banks x 16 pins) are available in the DADA SOM.
Description[edit | edit source]
Each channel in the GPIO modules has the following features:
- Supports 9 banks of 16 GPIO signals
- Supports up to 9 banks of interrupt capable GPIOs
- Interrupts:
- Can enable interrupts for each bank of 16 GPIO signals
- Interrupts can be triggered by rising and/or falling edge, specified for each interrupt capable GPIO signal
- Set/clear functionality: firmware writes 1 to corresponding bit position(s) to set or to clear GPIO signal(s). The firmware processes can toggle GPIO output signals without critical section protection
- Separate Input/Output registers: GPIO output signals can be toggled by direct write to the output register(s) in addition to set/clear
- output register reads in output drive status
Electrical, Thermal and Mechanical Features[edit | edit source]
Operational characteristics[edit | edit source]
Maximum ratings[edit | edit source]
| Parameter | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main power supply voltage | 3.1 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
Recommended ratings[edit | edit source]
| Parameter | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main power supply voltage | 3.135 | 3.3 | 3.465 | V |
Power consumption[edit | edit source]
Providing theoretical maximum power consumption value would be useless for the majority of system designers building their application upon DADA module. Practically speaking, these figures would be of no help when it comes to size power supply unit or to perform thermal design of real systems.
Instead, several configurations have been tested in order to provide figures that are measured on real-world use cases.
Please note that DADA platform is so flexible that it is virtually impossible to test for all possible configurations and applications on the market. The use cases here presented should cover most of real-world scenarios. However actual customer's application might require more power than values reported here or customer's use case may be differ significantly with respect to the ones here considered.
Therefore, application-specific requirements have always to be taken into consideration in order to size power supply unit and to implement thermal management properly.
Use cases results[edit | edit source]
| TBD |
The table below reports the power consumption measurements for the considered use cases.
| Checkpoint | Power (mW) (SOM) | Power (mW) |
|---|---|---|
| Idle U-Boot | --- | |
| Idle Linux | ||
| Suspend to RAM | ||
| Stress App test (*) @ 85°C |
(*) Stressful Application Test: eMMC, uSD and USB continuously copied + stressapptest + iperf eth0/eth1
Thermal management[edit | edit source]
The DADA SOM is designed to support the maximum available temperature range declared by the manufacturer.
The customer shall define and conduct a reasonable number of tests and verifications in order to qualify the DUT capabilities to manage the heat dissipation.
Any heatsink, fan etc shall be defined case by case.
DAVE Embedded Systems' team is available for any additional information, please contact sales@dave.eu.
Mechanical specifications[edit | edit source]
This chapter describes the mechanical characteristics of the DADA module.
SOM Layout[edit | edit source]
The following figure shows the physical dimensions of the DADA module:
Connectors[edit | edit source]
The following figure shows the DADA connector layout:
CAD drawings[edit | edit source]
- STEP (3D): [ https://www.dave.eu/links/p/6SVPhbS0xcoQY5QN CS093824A.step]
3D drawings[edit | edit source]