ZERO SOM/ZERO Evaluation Kit/pdf
Getting started[edit | edit source]
Kit Identification Codes[edit | edit source]
The development kits are identified by a couple of codes:
- P/N Part Number identification code
- S/N Serial Number identification code
These codes are printed on a label stuck to the box containing the kit.
For example, the following picture shows such a label of an ZERO Evaluation Kit with Serial Number 00A6
These codes are required to complete the registration process of the kit.
Unboxing[edit | edit source]
Once you've received the kit, please open the box and check the kit contents with the packing list included in the box, using the table on this chapter as a reference.
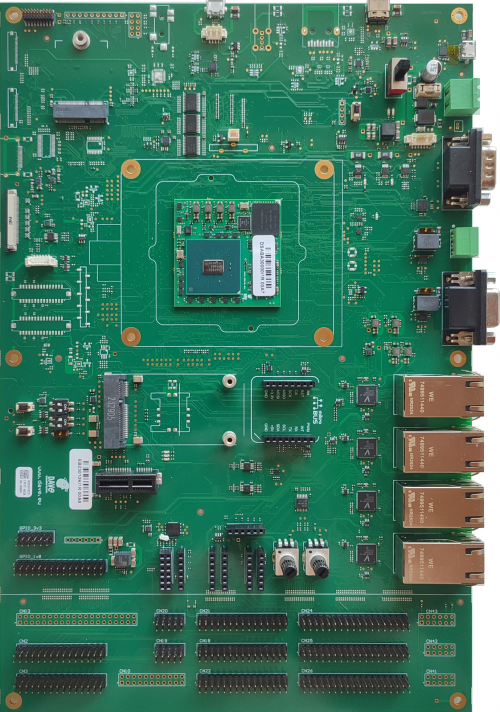
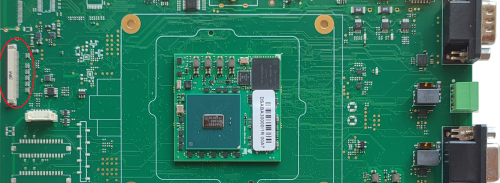
The hardware components (SOM and carrier board) are pre-assembled, as shown in the picture below:
Kit Contents[edit | edit source]
The following table list the kit components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| EB23 carrier board with ZERO SOM | |
| AC/DC Single Output Wall Mount adapter Output: +12V – 2.5 A | |
| Micro-USB to USB Type-A cable | |
| MicroSDHC card | |
| MIKROE-1203 Serial to USB adapter
(for 6-motors demo) | |
| Mini-USB to USB Type-A cable
(for 6-motors demo) |
Order codes[edit | edit source]
| Order code | Description |
|---|---|
| SDV4900000I1R-00 | This code refers to the default configuration detailed above including SOM DSABA30000I1R |
Connections[edit | edit source]
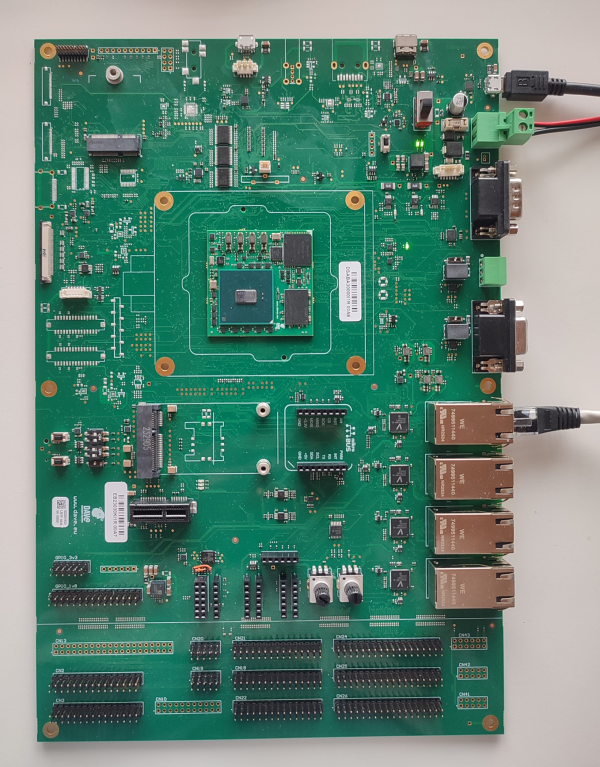
This section describes how to quick start the Evaluation Kit. The picture below shows the ZERO SOM Evaluation Kit:
The system is programmed to automatically boot Linux at power up, loading the bootloader, the kernel and device tree image and the root file system from the SD card memory.
To connect to the system:
- connect the 12Vcc power supply to J4 on the board
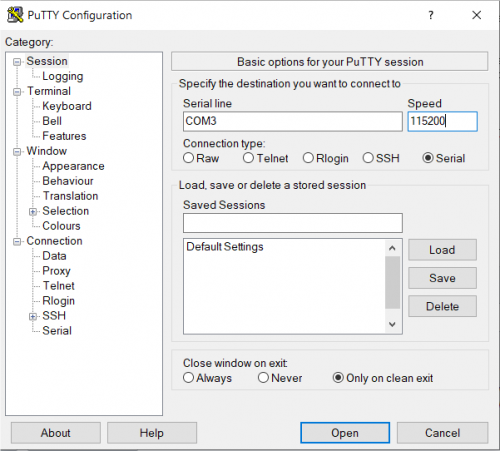
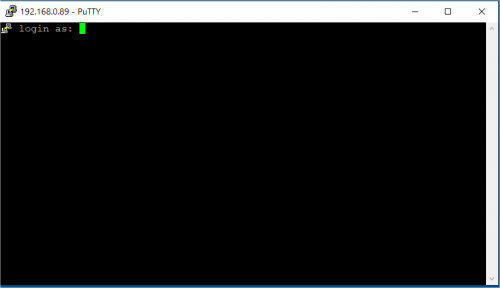
- start your favorite terminal emulator software on PC (eg: PuTTY, Minicom, ...); communication parameters are 115200,N,8,1
- (optional) connect the ethernet cable from your LAN hub/switch to the J19 ETH_A RJ45 connector
- start SSH, using the following parameters:
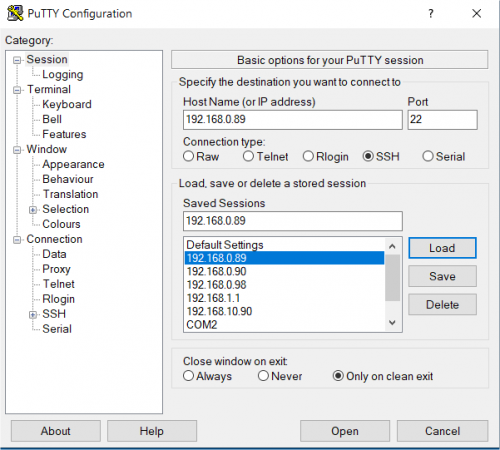
- ip address: 192.168.0.89
- username: root
- empty password
- start SSH, using the following parameters:
First boot[edit | edit source]
|
DESK-RZ-L Evaluation Kit has an hardware limitation on serial console debug cable. |
Once the EVK has been powered and reset, U-Boot bootloader will be executed and the debug messages will be printed on the serial console.
U-Boot automatically runs the autoboot macro, that loads the kernel/dtb and launches it with the options for mounting the root file system from the SD card.
At the end of the boot process, a demo application is launched and you can interact with the system using the touchscreen. The Linux shell is available on the serial console. Moreover, both telnet and ssh services are available to connect to the system through the network.
Serial console[edit | edit source]
A simple Windows serial and SSH/telnet client and terminal can be downloaded from here.
The following picture shows the serial setup for connecting to the EVK:
once selected the COM[x] serial port, click the Open button which starts the terminal. Once powered, the EVK shows the U-boot debug messages printed on the serial console.
Connecting through SSH[edit | edit source]
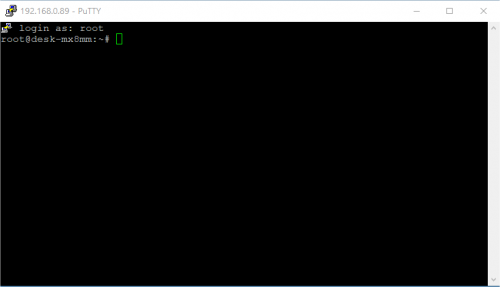
The following picture shows the SSH connection to the EVK:
once selected the IP address, click the Open button which starts the terminal. Once connected, the EVK shows the linux kernel prompt login for inserting the login:
Then use the root login username without password:
Reset Button[edit | edit source]
ZERO Evaluation Board has a push-button directly connected to the RESET_IN# signal which drives a SOM hardware reset.
S3 is the hardware reset button.
General Information[edit | edit source]
Product Highlights[edit | edit source]
The EB23 platform presented here provides a compact solution for any industry and can be easily interfaced with a 9-axis motor control interfaces and with a Plant Automation Control thanks to IEC-61131 SW language environment.
The following table summarises the main hardware and software features available with EB23:
Hardware[edit | edit source]
| Subsystem | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| CPU | Renesas RZ/T2H (OSM system-on-module) |
| USB | micro USB OTG 2.0 |
| Serial Ports | RS232 LVTTL UART CAN SPI |
| Ethernets | 10/100/1000Mbps |
| Connectivity | LTE (on mini-PCIe) and Wifi / BT (on M.2) |
| PCIe | M.2 and mini-PCIe |
| Display | RGB |
| Touchscreen | capacitive (on I2C bus) |
| Analog | ADC and PWM |
| Espansion | mikroBUS PMOD |
| PSU | 12 to 24V DC |
| Mechanical Dimensions | 250x300mm |
Software[edit | edit source]
| Subsystem | Options |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Linux, baremetal |
| Distribution | Yocto, Debian, Buildroot |
| Applications | Motor control, IoT |
Block diagram[edit | edit source]
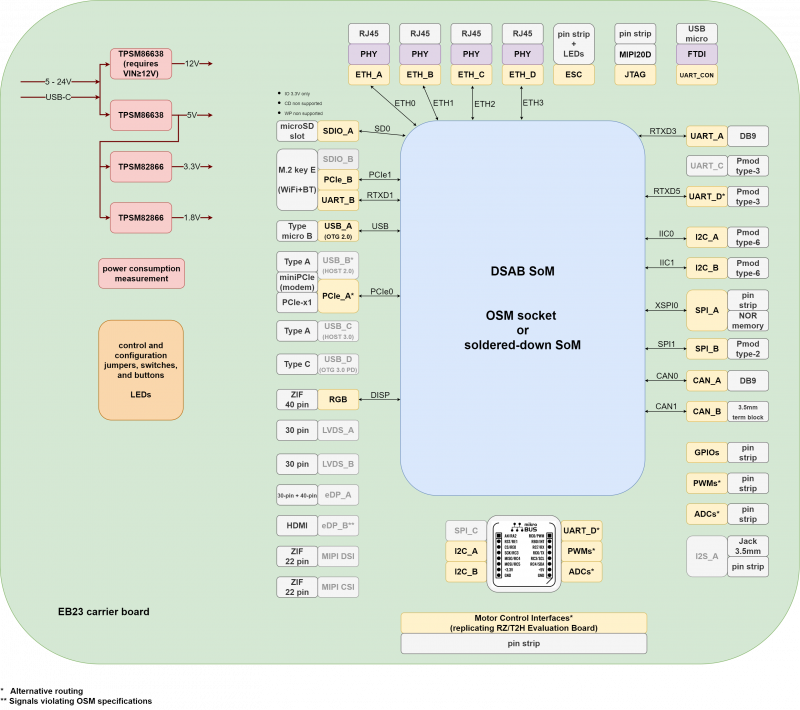
The following picture shows a simplified block diagram of the ZERO SOM Evaluation kit.
Main functional subsystems and interfaces are depicted.
The heart of the Evaluation Kit is the ZERO SOM module: please refer to the following Product Highlights page for the Evaluation Kit product highlights information.
Here below a summary for the main characteristics of the Kit.
Features Summary[edit | edit source]
| Feature | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Supported SOM | Renesas RZ/T2H |
| Serial bus | 1x UART RS232 1x UART LVTTL 2x CAN with PHY 1x SPI 1x xSPI |
| Connectivity | 3x Gigabit Ethernet on RJ45 connector 1x M.2 socket (for a Wireless module) 1x miniPCIe socket (for a LTE 4G modem) |
| Display | 1x LCD RGB-666 display interface |
| Storage | 1x microSD slot |
| USB | 1x USB 2.0 OTG port |
| Analog | 2x ADC channel 5x PWM output |
| Miscellaneous | Capacitive touch GPIOs JTAG RTC battery |
Electrical, Mechanical and Environmental Specifications[edit | edit source]
| Electrical / Mechanicals | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Supply voltage | + [12 - 24] V |
| Dimensions | 250 mm x 300 mm |
| Weight | 450 g |
| Operating Temperature | Industrial |
Interfaces and Connectors[edit | edit source]
Power Supply[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
Power is provided through the J4 connector. Power voltage range is +[12-24 V].
J4 is a two pins MSTBA 2.5/2-G-5.08 Phoenix connector.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
| Pin# | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | +[12-24 V] |
| 2 | DGND | Ground |
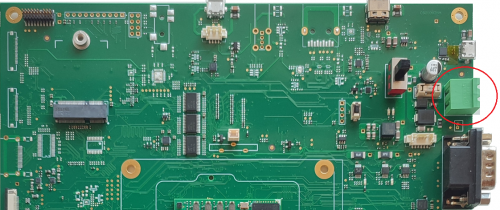
Power switch[edit | edit source]
The main power supply is enabled in the EB23 carrier board using the S1 power switch:
Power LEDs[edit | edit source]
DL2 and DL3 green LEDs show the status of the power input.
- DL2 is ON when a stable 5V power supply has been enabled
- DL3 is ON when a stable 3V3 power supply has been enabled
CPU connector[edit | edit source]
J1 is the OSM-L connector of the ZERO SOM.
In the ZERO Evaluation Kit, the SOM is soldered in the carrier board so the connector is not visible but represents the SOM J1 connector.
For a detailed description of the SOM pinout, please refer to the ZERO SOM SOM Hardware Manual.
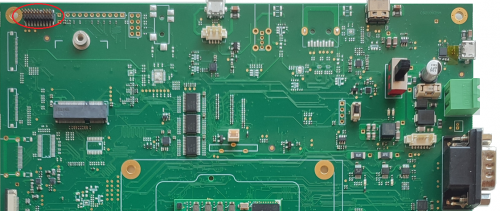
JTAG interface[edit | edit source]
JTAG interface allow the developer to access every peripheral of the SoC using a debugger.
Description[edit | edit source]
The JTAG interface available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J55.
J55 is a Samtec .050"x.050 terminale strip header connector (FTSH-110-01-L-DV-007).
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
| Pin# | Pin name | Function | ARM-20 JTAG | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VREF | - | 1 | 1V8 |
| 2 | JTAG_TMS | - | 7 | - |
| 4 | JTAG_TCK | - | 9 | - |
| 6 | JTAG_TDO | - | 13 | - |
| 8 | JTAG_TDI | - | 5 | - |
| 10 | JTAG_TRST | - | 15 | - |
| 12 | JTAG_RTCK | - | 11 | |
| 14,18,20 | N.C. | - | ||
| 3,5,9,11,13,15,17,19 | DGND | - | 4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20 | For example documented on Lauterbach specification |
(*) optional signals, keep the possibility to be unconnected.
Console interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
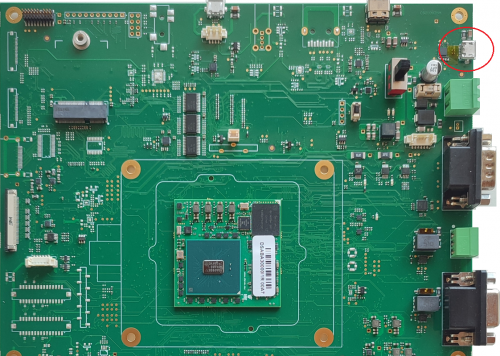
The Console interface is available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J7.
J7 is a micro USB connector for the two-wires SCI0 port used for debug purposes (bootloader and operating system serial console).
Signals[edit | edit source]
The interface signals related to the J7 connector are the standard USB signals available in a micro USB type AB connector.
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
SCI0 is mapped to /dev/ttySC0 device in Linux. The peripheral is used as the default serial console, both for the bootloader and the kernel.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
|
See the DESK-RZ-L-1.0.0 Known limitations about the console cable connection |
To connect to the debug serial port:
- power the Evaluation Kit on
- connect the micro USB side of the provided USB cable to the J7 connector on the EB23 carrier board
- start your favorite terminal emulator software on PC (eg: PuTTY); communication parameters are: 115200,N,8,1
- reset the EVK for receiving the power-on boot messages
Ethernet interfaces[edit | edit source]
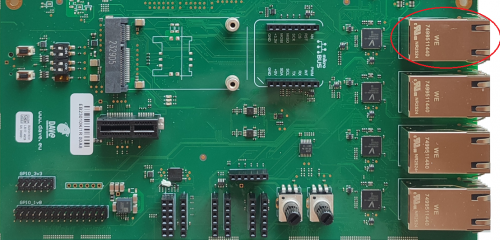
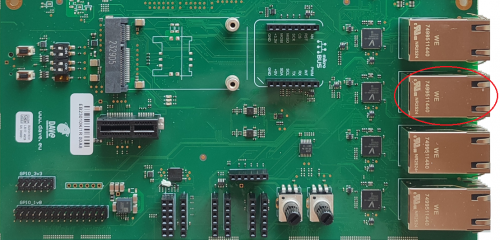
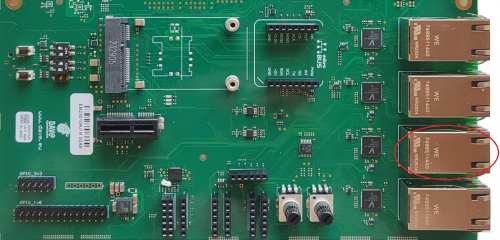
The ZERO Evaluation Kit features four Gigabit Ethernet interfaces with the PHY available in the EB23 carrier board.
Description[edit | edit source]
The Ethernet interfaces are available on the Evaluation Kit at the connectors J19 (ETH_A), J20 (ETH_B), J21 (ETH_C) and J22 (ETH_D).
Ethernet connectors are a RJ45 shielded connectors with dual led. The ethernet PHY is provided in the EB23 carrier board and the three SoC GMAC instances provide up to three ethernet interfaces.
The fourth ethernet interface (ETH_D) is available as EtherCAT or switch interface anf it is not used in the ZERO Evaluation Kit.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The interfaces signals mapping can be found in the Evaluation Kit schematics.
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
The network interfaces mapped as follows:
- J19 is
eth0device in Linux - J20 is
eth1device in Linux - J21 is
eth2device in Linux
Device usage[edit | edit source]
The peripherals use the standard kernel interface and network protocol stack.
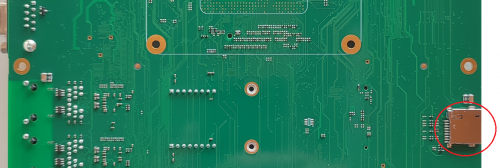
USB Ports interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
ZERO Evaluation Kit provides an USB OTG 2.0 type MicroB port through the J11 connector.
J11 is a micro-AB type receptacle for a USB OTG connection.
|
This interface if configured in Host mode mode through a mounting option. Other configuration can be used with an EB23 hardware modification. |
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interfaces signals:
| Pin# | OSM contact | OSM name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6, 7, 8, 9 | - | USB_OTG_SH Shield | ||
| 1 | AB16 | USB_A_VBUS | VBUS | |
| 2 | AB13 | USB_A_D_N | USB OTG Data - | |
| 3 | AC14 | USB_A_D_P | USB OTG Data + | |
| 4 | AB14 | USB OTG ID | USB_A_ID | |
| 5 | - | GND | Ground |
Device usage[edit | edit source]
The USB port can be used under Linux for connecting USB devices: the related device driver has to be integrated into the Linux kernel.
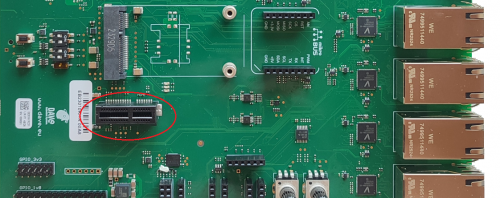
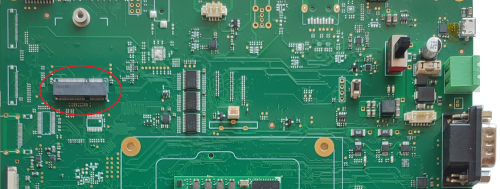
PCIe[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The two PCI Express lines are available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J15 and J18.
- J15 is a standard M.2 connnector dedicated to the WiFi module
- J18 is a standard 36 contacts female PCIe connector for a card edge PCIe module
Signals[edit | edit source]
Both connector interface signals respect the related M.2 and PCIe standards. The interfaces signals mapping can be found in the Evaluation Kit schematics.
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
The PCI express peripheral is mapped to the corresponding device in Linux depending on the associated kernel device driver and on the device tree configuration.
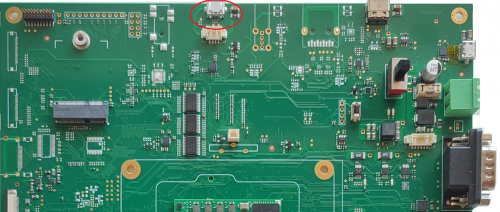
micro SD[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The micro SD interface available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J8.
J8 is a Micro-SD card header. This interface is connected to the sdhi0 controller of the RZ/T2H CPU.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
| Pin# | OSM contact | OSM name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H20 | SDIO_A_D2 | SDIO data 2 | |
| 2 | H21 | SDIO_A_D3 | SDIO data 3 | |
| 3 | E20 | SDIO_A_CMD | CMD | |
| 4 | - | 3V3 | +3.3 V | |
| 5 | F21 | SDIO_A_CLK | Clock | |
| 6 | - | DGND | Ground | |
| 7 | G20 | SDIO_A_D0 | SDIO data 0 | |
| 8 | G21 | SDIO_A_D1 | SDIO data 1 | |
| 9 | J21 | CD | Card detect | |
| 10, 11, 12, 13 | - | SD_SHIELD | Shield |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
The microSD card is mapped to /dev/mmcblk0. The available partitions are shown as /dev/mmcblk0p1, /dev/mmcblk0p2, etc.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
The device can be mounted/accessed as a standard block device in Linux.
LCD[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The LCD interface available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J30.
J30 is a 40-pin 0.5mm pitch FPC connector.
On this connector are routed the RGB signals interface that operates in the RGB-666 color mode.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interfaces signals:
| Pin# | OSM contact | OSM name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,2,12,16,20,24,28 32,36,37,39,40 |
- | DGND | Ground | |
| 4,5,6 | - | 5V | Power output | |
| 7,8 | - | 3V3 | Power output | |
| 10 | K3 | RGB_HSYNC | Horizontal sync | this pin is routed - by default - to GND (and not connected to HSYNC) |
| 11 | L3 | RGB_VSYNC | Vertical sync | this pin is routed - by default - to GND (and not connected to VSYNC) |
| 13 | M3 | RGB_B5 | B7 bit | |
| 14 | N4 | RGB_B4 | B6 bit | |
| 15 | M3 | RGB_B3 | B5 bit | |
| 17 | P3 | RGB_B2 | B4 bit | |
| 18 | R3 | RGB_B1 | B3 bit | |
| 19 | R4 | RGB_B0 | B2 bit | |
| 21 | T4 | RGB_G5 | G7 bit | |
| 22 | T3 | RGB_G4 | G6 bit | |
| 23 | U3 | RGB_G3 | G5 bit | |
| 25 | V4 | RGB_G2 | G4 bit | |
| 26 | V3 | RGB_G1 | G3 bit | |
| 27 | W4 | RGB_G0 | G2 bit | |
| 29 | Y4 | RGB_R5 | R7 bit | |
| 30 | Y5 | RGB_R4 | R6 bit | |
| 31 | AA5 | RGB_R3 | R5 bit | |
| 33 | Y6 | RGB_R2 | R4 bit | |
| 34 | AA6 | RGB_R1 | R3 bit | |
| 35 | Y7 | RGB_R0 | R2 bit |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
- LCD is typically mapped to
/dev/fb0device in Linux
Power sequence[edit | edit source]
Most of the LCD panels has many supplies and need a specific timing to power the rails and start the the signals.
The Evaluation Kit provides GPIO controlled power rails that can be leveraged both at bootloader and kernel level to meet any specifications.
The following sections describe the available rails:
+RGB_VDD[edit | edit source]
This is a 3V3 power rail, the most common voltage to supply the LCD panel internal logic. This rail is enabled by GPIO_C_5 that is connected to B_F4 OSM contact.
+RGB_5V[edit | edit source]
The most common voltage to supply the LCD panel backlight. This rail is enabled by GPIO_C_4 that is connected to B_F3 OSM ball.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
The display power sequence can be leveraged by a DAVE custom code that allow to set the timings both in U-boot and in Linux kernel sources.
The associated framebuffer device is accessed in Linux through the standard graphic access.
CAN[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
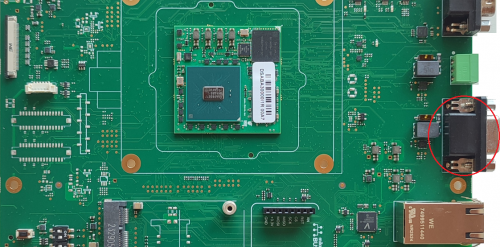
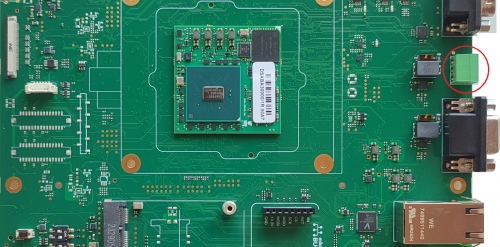
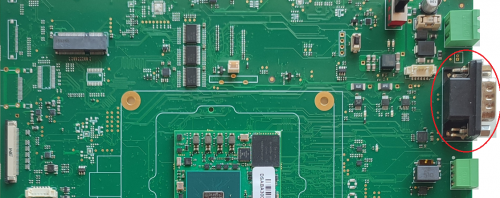
The CAN interface available on the Evaluation Kit at the connectors J35 and J36 that provides the CAN bus ports compatible with CAN FD 11898-1 standard.
- J35 is a DB9 female connector
- J36 is a Phoenix contact 3.5mm connector
The CAN transceivers are implemented on the EB23 carrier board.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
CAN_A[edit | edit source]
| Pin# | OSM contact | OSM name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,4,5,6,8,9 | - | N.A. | N.C. | |
| 2 | AB17 | CAN_A_RX | Low bus line | |
| 3 | - | DGND | Ground | |
| 7 | AC17 | CAN_A_TX | High bus line |
CAN_B[edit | edit source]
| Pin# | OSM contact | OSM name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AC19 | CAN_B_TX | High bus line | |
| 2 | AB19 | CAN_B_RX | Low bus line | |
| 3 | - | DGND | Ground |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
- CAN_A device is mapped to
can0device in Linux - CAN_B device is mapped to
can1device in Linux
The peripherals can be configured using ifconfig and ip link utilities.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
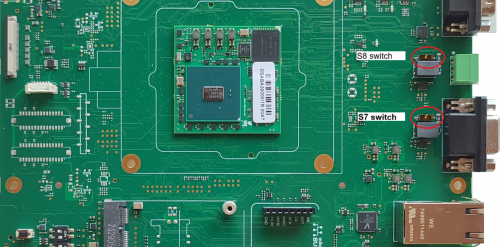
Set the switches S7 or S8 enables a 120Ω bus termination.
UARTs interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The UARTs interface available on the Evaluation Kit are mapped to the following connectors:
- J45 is a standard DB9 male connector for the RS232 UART port
- J44 is a 6x1x2.54mm female vertical socket header for the UART_D port. This is a Digilent Pmod™ Compatible connector for the UART Pmod™ Compatiblemodule (6-Pin Pmod™ Compatible Connector Digilent Pmod™ Interface Specification Type-3 UART)
- J43 is a 6x1x2.54mm female vertical socket header for the OSM-L UART_C port. This port is not available in the ZERO SOM
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following tables describes the interface signals
UART_A[edit | edit source]
| Pin# | OSM contact | OSM name | RS-232 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | Not connected | Not connected |
| 2 | A13 | UART_A_RX | UART_A receive line |
| 3 | B13 | UART_A_TX | UART_A transmit line |
| 4 | - | Not connected | Not connected |
| 5 | - | DGND | Ground |
| 6 | - | Not connected | Not connected |
| 7 | C13 | UART_A_RTS | UART_A Request To Send |
| 8 | C14 | UART_A_CTS | UART_A Clear To Send |
| 9 | - | Not connected | Not connected |
UART_D[edit | edit source]
| Pin# | OSM contact | OSM name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | - | |
| 2 | C23 | UART_D_TX | Transmit data | PMOD_A1 |
| 3 | C22 | UART_D_RX | Receive data | PMOD_A2 |
| 4 | - | - | - | |
| 5 | - | DGND | Ground | |
| 6 | - | 1V8 | +1.8 V |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
- UART_A is mapped to
/dev/ttySC3device in Linux - UART_D is mapped to
/dev/ttySC5device in Linux
Device usage[edit | edit source]
- UART_A supports the RS232 protocol
- UART_D can be used with a PMOD Type-3 adapter or with a LVTTL peripheral
ADCs[edit | edit source]
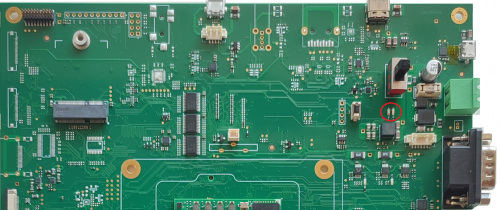
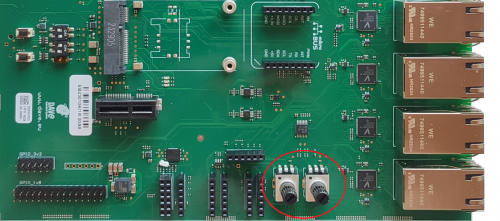
The ADC interface is connected to two analog potentiometers in the EB23 carrier board.
Description[edit | edit source]
The two potentiometers are visible in the picture here below:
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
| OSM contact | OSM name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| M18 | ADC_0 | Analog channel 0 | |
| N18 | ADC_1 | Analog channel 1 |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
The ADC peripheral is mapped to the adc2/iio interface in Linux.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
The peripheral is used by the ADC kernel interface as documented in the DESK-RZ-L wiki page.
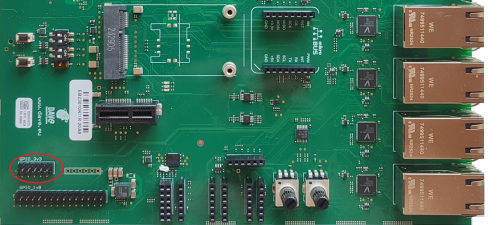
GPIOs interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
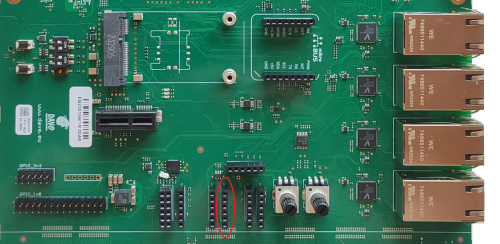
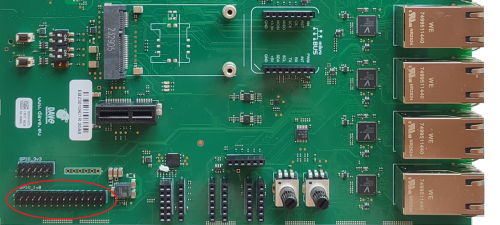
The GPIOs interface is available on the Evaluation Kit at the connectors CN1 and J54.
- CN1 is a 15x2x2.54mm pinstrip header connector and it mades availability OF GPIO_A to GPIO_E OSM contacts. GPIOs are at 1V8 voltage level
- J54 is a 6x2x2.54mm pinstrip header connector and it mades available a set of GPIOs through and I2C expander and they are at 3V3 voltage level
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
CN1[edit | edit source]
| Pin# | OSM name | OSM contact | Pin name | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | +1V8 | |
| 2 | - | - | +1V8 | |
| 3 | E17 | GPIO_A_1 | OPT_GPIO_A_1 | optionally available |
| 4 | V32 | GPIO_D_2 | OPT_GPIO_D_2 | optionally available |
| 5 | G17 | GPIO_A_3 | GPIO_A_3 | |
| 6 | V33 | GPIO_D_3 | OPT_GPIO_D_3 | optionally available |
| 7 | H17 | GPIO_A_4 | OPT_GPIO_A_4 | optionally available |
| 8 | W32 | GPIO_D_4 | OPT_GPIO_D_4 | optionally available |
| 9 | J17 | GPIO_A_5 | GPIO_A_5 | |
| 10 | W33 | GPIO_D_5 | OPT_GPIO_D_5 | optionally available |
| 11 | E19 | GPIO_B_1 | OPT_GPIO_B_1 | optionally available |
| 12 | Y32 | GPIO_D_6 | OPT_GPIO_D_6 | optionally available |
| 13 | G19 | GPIO_B_3 | GPIO_B_3 | |
| 14 | AF32 | GPIO_E_0 | GPIO_E_0 | |
| 15 | J19 | GPIO_B_5 | GPIO_B_5 | |
| 16 | AF33 | GPIO_E_1 | OPT_GPIO_E_1 | optionally available |
| 17 | K19 | GPIO_B_6 | OPT_GPIO_B_6 | optionally available |
| 18 | AG32 | GPIO_E_2 | GPIO_E_2 | |
| 19 | L19 | GPIO_B_7 | OPT_GPIO_B_7 | optionally available |
| 20 | AG33 | GPIO_E_3 | GPIO_E_3 | |
| 21 | D3 | GPIO_C_0 | OPT_GPIO_C_0 | optionally available |
| 22 | AH32 | GPIO_E_4 | GPIO_E_4 | |
| 23 | D4 | GPIO_C_1 | OPT_GPIO_C_1 | |
| 24 | AH33 | GPIO_E_5 | OPT_GPIO_E_5 | optionally available |
| 25 | U32 | GPIO_D_0 | OPT_GPIO_D_0 | optionally available |
| 26 | AJ32 | GPIO_E_6 | OPT_GPIO_E_6 | optionally available |
| 27 | U33 | GPIO_D_1 | OPT_GPIO_D_1 | optionally available |
| 28 | AJ33 | GPIO_E_7 | OPT_GPIO_E_7 | optionally available |
| 29 | - | - | DGND | |
| 30 | - | - | DGND |
J54[edit | edit source]
| Pin# | Pin name | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GPIO_3V3_01 | |
| 2 | +3V3 | |
| 3 | GPIO_3V3_02 | |
| 4 | GPIO_3V3_06 | |
| 5 | GPIO_3V3_03 | |
| 6 | ETH_A_RST | ETH_A phy reset signal |
| 7 | GPIO_3V3_04 | |
| 8 | ETH_B_RST | ETH_B phy reset signal |
| 9 | GPIO_3V3_05 | |
| 10 | ETH_C_RST | ETH_C phy reset signal |
| 11 | DGND | Ground |
| 12 | ETH_D_RST | ETH_D phy reset signal |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
GPIOs can be used directly on Linux kernel device driver or can be configured on the device tree.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
Electrical and Mechanical Documents[edit | edit source]
Schematics[edit | edit source]
Please find here below the links for the ZERO Evaluation Kit schematics and the related documents (BOM and layout):
Layout[edit | edit source]
Mechanical specifications[edit | edit source]
This page describes the mechanical characteristics of the ZERO EvaluationKit carrier board.
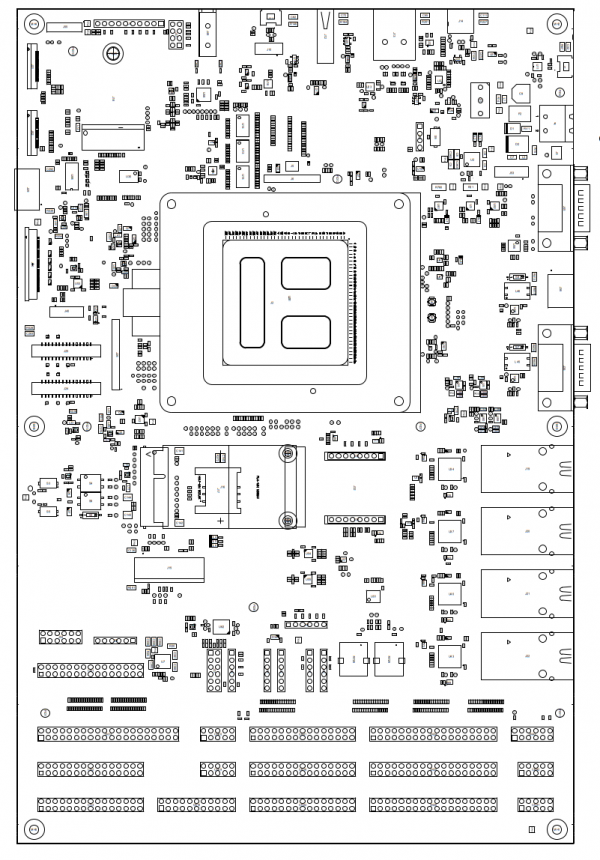
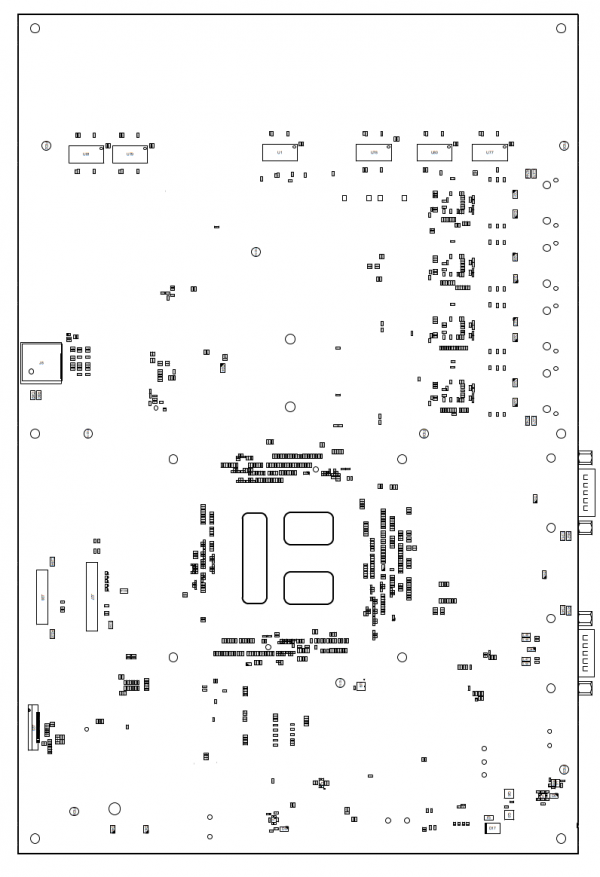
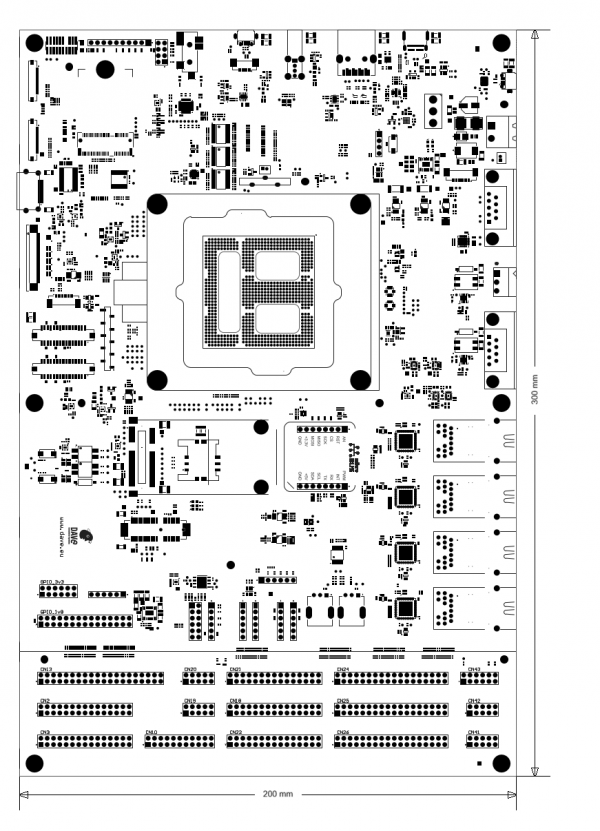
Board layout[edit | edit source]
ZERO Evaluation Kit assembly view
Dimensions[edit | edit source]
Mechanical data[edit | edit source]
| Dimension | Value |
|---|---|
| Width | 200 mm |
| Depth | 300 mm |
| Max component's height (top) | 20.35 mm |
| Max component's height (bottom) | 2.40 mm |
| PCB height | 1.65 mm |