ETRA SOM/ETRA Evaluation Kit/pdf
Contents
- 1 Getting started
- 2 General Information
- 3 Interfaces and Connectors
- 4 Electrical and Mechanical Documents
Getting started[edit | edit source]
Kit Identification Codes[edit | edit source]
The development kits are identified by a couple of codes:
- P/N Part Number identification code
- S/N Serial Number identification code
These codes are printed on a label stuck to the box containing the kit.
For example, the following picture shows such a label of an AXEL Lite Evaluation Kit with Serial Number 0DE7
These codes are required to complete the registration process of the kit.
Unboxing[edit | edit source]
Once you've received the kit, please open the box and check the kit contents with the packing list included in the box, using the table on this chapter as a reference.
The hardware components (SOM, carrier boards and display) are pre-assembled, as shown in the picture below:
Kit Contents[edit | edit source]
The following table list the kit components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
ETRA SBC
| |
| Ampire AM-800480BTMQW-TBMH-A 7” 800x480 RGB display | |
| AC/DC Single Output Wall Mount adapter Output: +12V – 2.0 A | |
| FTDI TTL/USB cable (TTL-232RG-VIP-WE) | |
| MicroSDHC card |
Order codes[edit | edit source]
| Order code | Description |
|---|---|
| SDCSB70000D1R-00 | This code refers to the default configuration detailed above including SOM S-DSDAE09300I1R |
microSD Layout[edit | edit source]
The microSD provided with the kit is used to store:
- a bootable partition (mmcblk0p1, vfat) containing:
- binary images (u-boot and kernel images)
- root file system partition (mmcblk0p2, ext4)
Connections[edit | edit source]
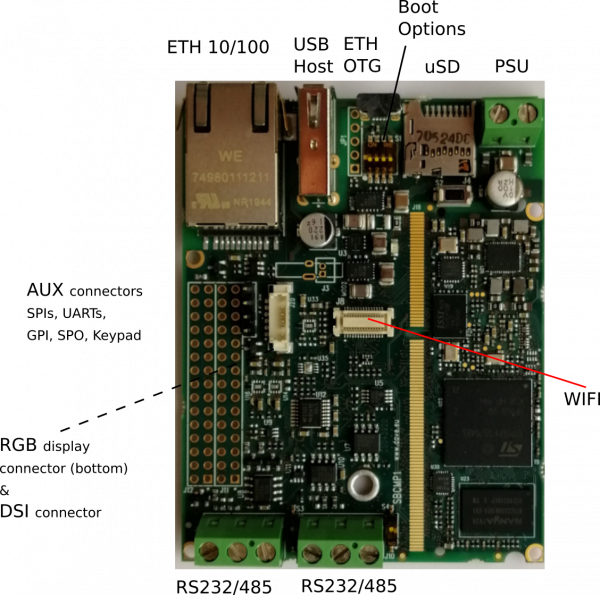
This section describes how to quick start the Evaluation Kit. The picture below shows the ETRA SOM inserted into the Evaluation Kit:
The system is programmed to automatically boot Linux at power up, loading the bootloader, the kernel and device tree image and the root file system from the SD card memory.
To connect to the system:
- insert the SD card into the micro SD slot
- connect the 12Vcc power supply to J1 on the board
- connect the USB to TTL UART adapter to the J2 connector on the SBC and connect the USB side connector to an USB port on your computer
- if required, install the FTDI USB to serial driver
- start your favorite terminal emulator software on PC (eg: PuTTY, Minicom, ...); communication parameters are 115200,N,8,1
- (optional) connect the ethernet cable from your LAN hub/switch to the J5 RJ45 connector
- start SSH, using the following parameters:
- ip address: 192.168.0.89
- username: root
- empty password
- start SSH, using the following parameters:
Warning: please, pay attention to the debug cable header connection, see the picture here below:
First boot[edit | edit source]
Once power has been applied, U-Boot bootloader will be executed and the debug messages will be printed on the serial console. U-Boot automatically runs the autoboot macro, that loads the kernel/dtb and launches it with the options for mounting the root file system from the SD card.
At the end of the boot process, a demo application is launched and you can interact with the system using the touchscreen. The Linux shell is available on the serial console. Moreover, both telnet and ssh services are available to connect to the system through the network.
Serial console[edit | edit source]
A simple Windows serial and SSH/telnet client and terminal can be downloaded from here.
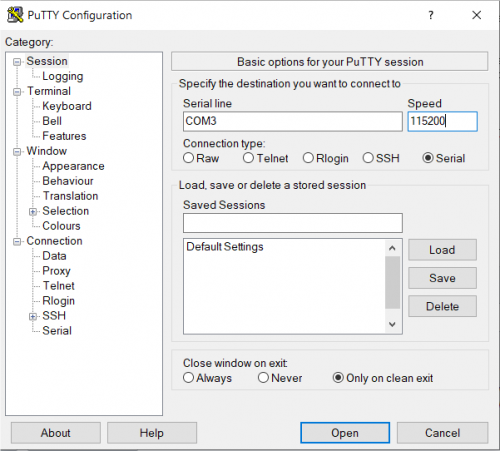
The following picture shows the serial setup for connecting to the EVK:
once selected the COM[x] serial port, click the Open button which starts the terminal. Once powered, the EVK shows the U-boot debug messages printed on the serial console.
Connecting through SSH[edit | edit source]
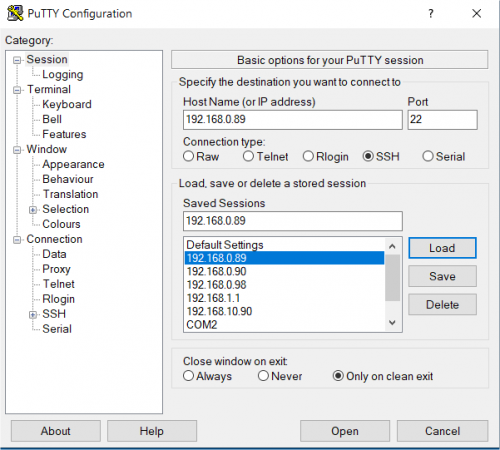
The following picture shows the SSH connection to the EVK:
once selected the IP address, click the Open button which starts the terminal. Once connected, the EVK shows the linux kernel prompt login for inserting the login:
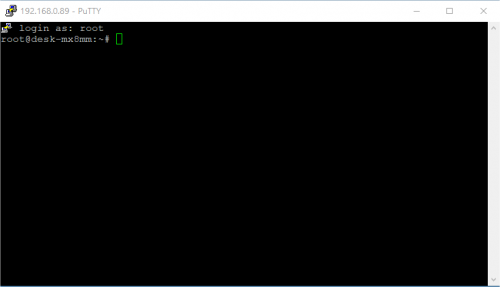
Then use the root login username without password:
Boot Configurations[edit | edit source]
ETRA Evaluation Board is built upon STM32MP1 processor.
The following sections detail boot configuration options, which differ depending on the SoM.
Available options[edit | edit source]
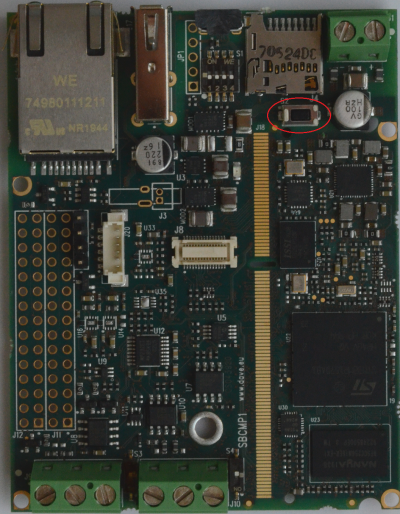
Boot modes can be selected by S1 DIP-switch which acts directly on BOOT_MODE[2..0] configuration pins.
S1 switches are connected to ETRA BOOT_MODE[2:0] pins allowing different boot modes.
where S1 switches are mapped as the following table:
| BOOT_MODE | S1 | Note |
|---|---|---|
| BOOT_MODE0 | S1.1 | |
| BOOT_MODE1 | S1.2 | |
| BOOT_MODE2 | S1.3 | |
| - | S1.4 | USB OTG settings |
DIP settings[edit | edit source]
| BOOT_MODE[2:0] | S1[3..1] | Boot peripheral | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 000 | OFF-OFF-OFF | USB | boot from USB OTG |
| 001 | OFF-OFF-ON | NOR | boot from NOR flash on Quad-SPI |
| 010 | OFF-ON-OFF | eMMC | boot from eMMC on SDMMC2 |
| 101 | ON-OFF-ON | SD | Default boot from SD card on SDMMC1 |
| 111 | ON-ON-ON | NAND | boot from NAND flash on Quad-SPI |
Reset Button[edit | edit source]
ETRA Evaluation Board has a pushbutton directly connected to the PMIC.RSTN signal which drives a PMIC hardware reset.
S2 is the hardware reset button.
General Information[edit | edit source]
Product Highlights[edit | edit source]
The SBC ETRA platform presented here provides a compact solution for any industry and can be easily interfaced with Plant Automation Control thanks to IEC-61131 SW language environment and/or other plug-ins like QT framework or multimedia GStreamer video applications.
The following table summarizes the main hardware and software features available with SBC ETRA:
Hardware[edit | edit source]
| Subsystem | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| CPU | STMicroelectronics STM32MP1 Solo/Dual core |
| USB | Host and OTG |
| Storage | onboard eMMC or NAND, uSD connector |
| Serial Ports | dual RS232/485 port |
| Ethernet | 10/100Mbps |
| Display | WIDE™ interface with 18- or 24-bit RGB |
| Video | 2 lane MIPI interface |
| Touchscreen | USB capacitive |
| Connectivity | Bluetooth and Wi-Fi |
| LED and Buttons | (optional) membrane with up to 6 LED and 2 buttons |
| PSU | 12 to 24V DC or 5V from USB |
| Mechanical Dimensions | 87x68mm - Standard DIN (4modules) |
Software[edit | edit source]
| Subsystem | Options |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Linux |
| Distribution | Yocto |
| Graphical Framework | Qt |
Block diagram[edit | edit source]
The following picture shows a simplified block diagram of the ETRA SOM Evaluation kit.
Main functional subsystems and interfaces are depicted.
The heart of the Evaluation Kit is the ETRA SOM module: please refer to the following Product Highlights page for the Evaluation Kit product highlights information.
Here below a summary for the main characteristics of the Kit.
Features Summary[edit | edit source]
| Feature | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Supported SOM | integrated on carrier board |
| Serial Ports | 2x UART RS232/RS485 1x LVTTL UART on pin strip (debug port) |
| Connectivity | 1x 10/100TX Ethernet on RJ45 connector DWM Wireless module (optional) |
| Display | WIDE™ display interface
2 lane MIPI interface |
| Storage | 1x microSD slot
1x eMMC on board device (optional) |
| USB | 1x USB 2.0 Host port 1x USB OTG port |
| Miscellaneous | Capacitive touchscreen connector GPIOs ADCS DACs user LED and Buttons (optional) |
Electrical, Mechanical and Environmental Specifications[edit | edit source]
| Electrical / Mechanicals | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Supply voltage | + [12 - 24] V or +5V from USB OTG port |
| Dimensions | 86 mm x 68 mm |
| Weight | TBD g |
| Operating Temperature | -5/+65 °C |
Interfaces and Connectors[edit | edit source]
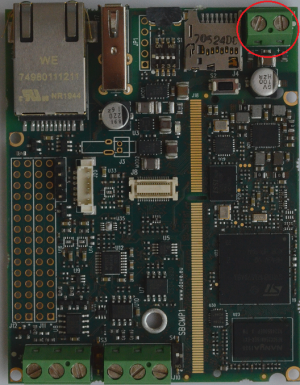
Power Supply[edit | edit source]
The power supply for this EVB can be provided through J1 connector or from USB OTG connector.
Description[edit | edit source]
Power can be provided through the J1 connector. Power voltage range is +[12-24 V].
J1 is a two pins MSTBA 2.5/2-G-5.08 Phoenix connector.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
| Pin# | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | +[12-24 V] |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
Power LED[edit | edit source]
DL1 is a green LED (placed near the SOM) it shows the status of the power input. This LED is ON when a valid power supply is present either from J1 or USB OTG port.
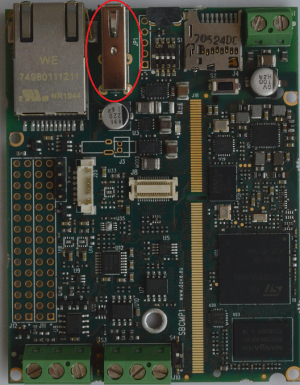
CPU connector[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
J18 is the 204-pin SODIMM connector of the ETRA SOM.
In this SBC design, the SOM is embedded in the carrier board so the connector is not actually usable but represents the SOM J1 connector.
For a detailed description of the SOM pinout, please refer to the ETRA SOM Hardware Manual SO-DIMM connector.
JTAG interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The JTAG interface is available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J11.
J11 is a 30 pin (2x15x2.54mm) header connector and is also used for expansion signlas.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals on J11 connector:
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | J18.62 | VDD | VDD | reference voltage |
| 19 | J18.90 | JTMS-SWDIO | JTMS-SWDIO | |
| 21 | J18.98 | JTCK-SWCLK | JTCK-SWCLK | |
| 23 | J18.92 | JTDI | JTDI | |
| 25 | J18.96 | JTDO-TRACESWOO | JTDO-TRACESWOO | |
| 27 | J18.94 | NJTRST | NJTRST |
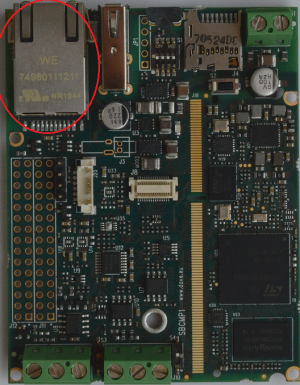
Ethernet interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The Ethernet interface is available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J5.
J5 is a standard RJ45 connector connected to the SOM integrated ethernet controller and PHY.
J6 and J7 connectors are pin-to-pin compatible mounting options for the same interface.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals on J18 SOM connector:
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | J18.19 | ETH_TX_P | Transmit data + | |
| 5 | J18.21 | ETH_TX_M | Transmit data - | |
| 6 | J18.23 | ETH_RX_P | Receive data + | |
| 8 | J18.25 | ETH_RX_M | Receive data - | |
| 2,11 | J18.13 | ETH1_LED | Eth link or activity led |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
This network interface is mapped at eth0 device in Linux.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
The peripheral is used the standard kernel interface and network protocol stack.
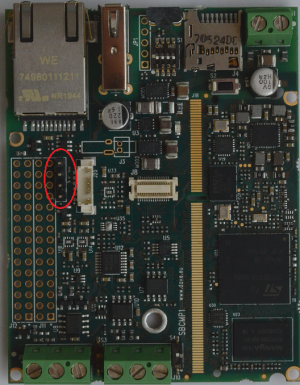
Console interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The Console interface available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J2.
J2 is a 4 pin (4x1x2.54mm) header connector for the two-wires USART1 port, used for debug purposes (bootloader and operating system serial console).
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | J18.187 | UART TX | Transmit line | |
| 2 | J18.189 | UART RX | Receive line | |
| 3 | - | 3V3_CB | Power output | This pin can be used to power an RS232 transceiver |
| 4 | - | DGND | Ground |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
USART1 is mapped to /dev/ttySTM0 device in Linux. The peripheral is used as the default serial console, both for the bootloader and the kernel.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
To connect to the debug serial port:
- connect the UART to USB transceiver to J2 connector
- start your favorite terminal emulator software on PC (eg: PuTTY); communication parameters are: 115200,N,8,1
UARTs interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The UART interfaces are available on the Evaluation Kit at the connectors J9 and J10.
J9 and J10 are 3 pin terminal blocks 5.0mm pitch respectively for USART3 and UART8. Can be independently used as RS232 or RS485 based on Part Number composition.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
J9[edit | edit source]
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | RS232 | RS485 | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | J18.89 | USART3_TX | RS485_A | |
| 2 | J18.91 | USART3_RX | RS485_B | |
| 3 | - | Ground | Ground |
J10[edit | edit source]
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | RS232 | RS485 | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | J18.191 | UART8_TX | RS485_A | |
| 2 | J18.193 | UART8_RX | RS485_B | |
| 3 | - | Ground | Ground |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
USART3 is mapped to /dev/ttySTM1 device in Linux.
UART8 is mapped to /dev/ttySTM2 device in Linux.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
Fix the signal cables to the terminal with a small flat screwdriver.
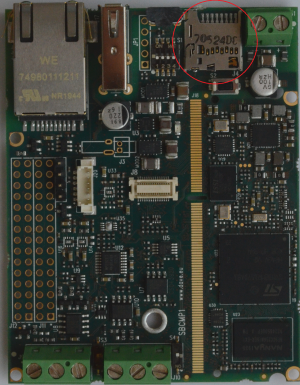
micro SD interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The micro SD interface available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J4.
J4 is a Micro-SD card header. This interface is connected to the SDMMC1 controller of the STM32MP1 CPU.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | J18.79 | PE6 | Data 1 | |
| 2 | J18.81 | PC11 | Data 3 | |
| 3 | J18.83 | PD2 | CMD | |
| 4 | - | 3V3_SD | +3.3 V | |
| 5 | J18.85 | PC12 | Clock | |
| 6, 10 | - | DGND | Ground | |
| 7 | J18.75 | PC8 | Data 0 | |
| 8 | J18.77 | PC9 | Data 1 | |
| 11, 12, 13, 14 | - | PCB_GND_RNG | Shield | |
| 9 | J18.177 | PE9 | Card detect |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
The microSD card is mapped to /dev/mmcblk1. The available partitions are available as /dev/mmcblk1p8, /dev/mmcblk1p9, /dev/mmcblk1p10, etc.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
The device can be mounted/accessed as a standard block device in Linux.
USB ports[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
ETRA SBC provides two USB ports, one HOST and one OTG:
- J17 is a standard USB HOST 2.0 Type A connector
- J16 is a micro-AB type receptacle for a USB OTG connection: this interface can operate in Host mode and Device (peripheral) mode
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
USB HOST[edit | edit source]
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | J18.188 | USB_HOST_VBUS | VBUS | |
| 2 | J18.202 | USB_DM1 | USB Host Data - | |
| 3 | J18.200 | USB_DP1 | USB Host Data + | |
| 4 | - | DGND | Ground | |
| 5, 6, 7, 8 | - | PCB_GND_RNG | Shield |
USB OTG[edit | edit source]
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | J18.185 | VBUS_OTG_IN | VBUS | Can be used to power the board |
| 2 | J18.196 | USB_DM2 | USB OTG Data - | |
| 3 | J18.198 | USB_DP2 | USB OTG Data + | |
| 4 | J18.72 | PA8 | USB OTG ID | |
| 5 | - | GND | Ground | |
| 6, 7, 8 | - | PCB_GND_RNG | Shield |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
The USB Host port can be used under Linux for connecting USB peripheral devices: the related peripheral driver has to be integrated into the Linux kernel.
The USB OTG feature can be easily tested using the Mass Storage Gadget driver.
ETRA SOM/ETRA Evaluation Kit/Interfaces and Connectors/LVDS
Touchscreen interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The Touchscreen interface is available on USB or I2C interface connectors.
ETRA Evaluation Kit uses, by default, the USB interface for connecting the touchscreen controller. Anyway, the I2C interface is available too and - optionally - can be activated in the device tree for enabling the I2C touch controller driver.
USB touchscreen[edit | edit source]
The USB OTG port - available on J16 connector - is configured as USB Host controller for driving the touchscreen. For this purpose, it is required to enable the USB OTG ID signals a low. This can be possible using the S1.4 DIP switch which forces the ID signal as low:
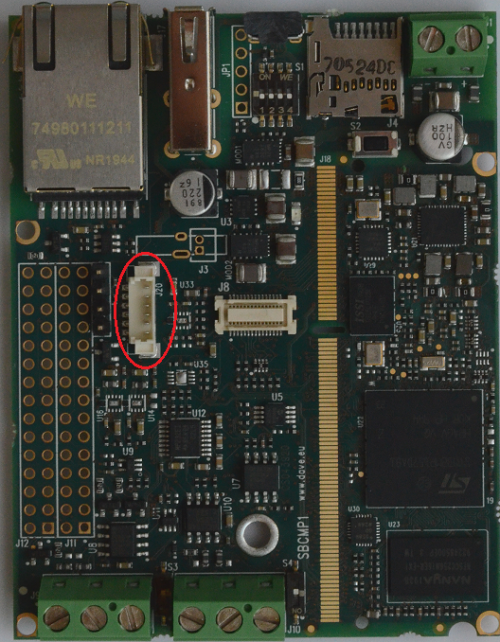
I2C touchscreen[edit | edit source]
The I2C touchscreen interface is available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J20. J20 is a 6-pin Molex PicoBlade connector for the I2C and control signals needed by most of the capacitive TSC.
This interface can be configured to work with 3.3V (default) or 5V power and signal levels.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | DGND | Ground | |
| 2 | J18.48 | TOUCH_SDA | I2C_SDA | |
| 3 | J18.38 | TOUCH_SCL | I2C_SCL | |
| 4 | J18.101 | TOUCH_VDD | TSC power | powered through a control switch |
| 5 | J18.201 | TOUCH_INT | TSC interrupt | input |
| 6 | J18.199 | TOUCH_RES | TSC reset | output |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
The device is typically mapped to /dev/touchscreen0 device in Linux.
The touch controller is attached to the generic Linux input event interface (evdev).
Device usage[edit | edit source]
The simplest tools for touch screen management are the tslib library and ts_tools utilities. To calibrate the touch screen, the ts_calibrate command line tool is available. After calibration, the touch screen can be tested using the graphical ts_test utility or the ts_print command line tool.
ETRA SOM/ETRA Evaluation Kit/Interfaces and Connectors/HDMI
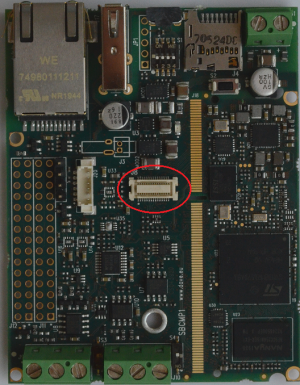
MIPI interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
The MIPI Display serial Interface interface available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J19
J19 is a 10 pin ZIF connector (0.5mm pitch, bottom contacts) for the DSI interface.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | DGND | Ground | |
| 2 | J18.121 | DSI_D1P | data lane1 + | |
| 3 | J18.119 | DSI_D1N | data lane1 - | |
| 4 | - | DGND | Ground | |
| 5 | J18.117 | DSI_D0P | data lane0 + | |
| 6 | J18.115 | DSI_D0N | data lane0 - | |
| 7 | - | DGND | Ground | |
| 8 | J18.113 | DSI_CKP | clock + | |
| 9 | J18.111 | DSI_CKN | clock - | |
| 10 | - | DGND | Ground |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
The MIPI CSI peripheral is mapped to the corresponding /dev/video<X> device in Linux. The device mapping depends on the device tree configuration.
ETRA SOM/ETRA Evaluation Kit/Interfaces and Connectors/PCIe ETRA SOM/ETRA Evaluation Kit/Interfaces and Connectors/CAN ETRA SOM/ETRA Evaluation Kit/Interfaces and Connectors/Audio
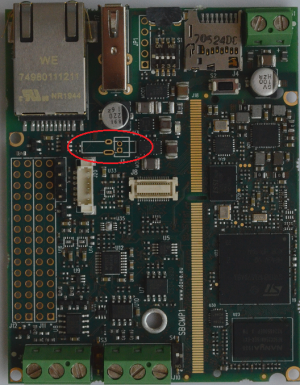
RTC device[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
There are two RTC devices on the Evaluation Kit, one is provided by the STM32MP1 SoC, the other is a Maxim DS3232M I2C device.
Both RTC can retain time and custom data over blackouts using a backup power source as:
- the lithium rechargeable battery (BT1) optionally mounted on the carrier board
- an external battery connected to J3 (alternate mounting option to the battery)
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals for J3:
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | J18.14 | VBAT | can be configured for battery connection | |
| 2 | - | DGND | Ground |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
RTC is mapped to /dev/rtc0 device in Linux.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
The peripheral can be accessed through the date and hwclock linux commands.
DWM[edit | edit source]
DWM is a Dave Wireless Module, more detail at the DWM page.
Description[edit | edit source]
The DWM interface is available on the Evaluation Kit at the connector J8.
J8 is a 30-pins 0.50mm Pitch SlimStack™ Receptacle. This connector is dedicated to the DWM (optional) add-on module.
The module is built around an LS Research TiWi-BLE Integrated Transceiver Modules for WLAN 802.11 b/g/n and Bluetooth.
The module implements the necessary PHY/MAC layers to support WLAN applications in conjunction with a host processor over a SDIO interface. The module also provides a Bluetooth platform through the HCI transport layer. Both WLAN and Bluetooth share the same antenna port.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes the interface signals:
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 2 | - | 5V_CB | 5V power | |
| 3, 4 | - | 3V3_CB | 3.3V power | |
| 5, 6, 9, 10, 19 | - | DGND | Ground | |
| 7 | J18.45 | WIFI_CMD | ||
| 8 | J18.47 | WIFI_CLK | ||
| 11 | J18.37 | WIFI_DATA0 | ||
| 13 | J18.39 | WIFI_DATA1 | ||
| 15 | J18.41 | WIFI_DATA2 | ||
| 17 | J18.43 | WIFI_DATA3 | ||
| 21 | J18.80 | BT_UART_RX | Used only for BT peripheral | |
| 23 | J18.76 | BT_UART_CTS | Used only for BT peripheral | |
| 24 | J18.105 | TIWI_BT_F5 | ||
| 25 | J18.74 | BT_UART_TX | Used only for BT peripheral | |
| 26 | J18.72 | TIWI_BT_F2 | ||
| 27 | J18.78 | BT_UART_RTS | Used only for BT peripheral | |
| 28 | J18.70 | TIWI_IRQ | ||
| 29 | J18.51 | TIWI_BT_EN | ||
| 30 | J18.53 | TIWI_EN | ||
| 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22 | - | N.C. | Not connected |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
| Section not completed yet |
The WiFi peripheral is mapped to the corresponding wlan<X> device in Linux. The network peripheral is visible under the ifconfig network configuration utility.
The BT peripheral is mapped to /dev/ttyxxx device in Linux.
The control signals are managed by rfkill in Linux.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
The WiFi peripheral use the standard kernel interface and network protocol stack.
The BT peripheral use the standard kernel hci interface.
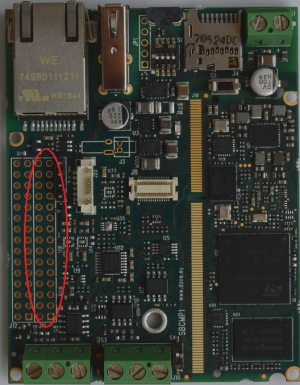
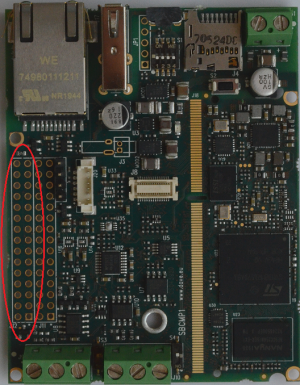
GPIOs interface[edit | edit source]
Description[edit | edit source]
STM32MP1 can handle external pins in many different ways and most of them can be configured as GPIOs. When a pin is set as a GPIO, it is possible to read its value, change its direction or change output value directly from the shell.
Signals[edit | edit source]
The following table describes some GPIOs signals available on J12 (2x15x2.54mm) connector:
| Pin# | SOM Pin# | Pin name | Pin function | Pin Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | J18.97 | PD13 | ||
| 5 | J18.99 | PD12 | ||
| 6 | J18.34 | PB13 | ||
| 7 | J18.101 | PD11 | ||
| 8 | J18.68 | PB5 | ||
| 9 | J18.105 | PG9 | ||
| 12 | J18.48 | PA12 | ||
| 14 | J18.38 | PA11 | ||
| 18 | J18.80 | PF6 | ||
| 20 | J18.76 | PF9 | ||
| 22 | J18.74 | PF7 | ||
| 24 | J18.78 | PF8 | ||
| 26 | J18.181 | PD6 | ||
| 28 | J18.28 | PA9 |
Device mapping[edit | edit source]
GPIOs can be used directly on Linux kernel device driver or can be configured on the device tree.
Device usage[edit | edit source]
See the GPIOs page on the DESK-MP1-L Software Manual.
Electrical and Mechanical Documents[edit | edit source]
Please find here below the links for the ETRA Evaluation Kit schematics and the related documents (BOM and layout).
|
Please note that SBC ETRA has been built around the ETRA SOM: on page 12 there is the SO-DIMM connector which separates the inside SOM core vs the external SBC. The SOM schematics are reserved and not published as documentation. |
Schematics[edit | edit source]
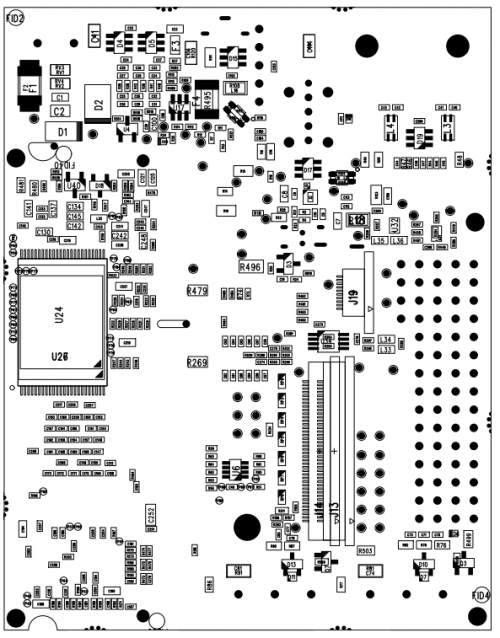
Layout[edit | edit source]
Mechanical specifications[edit | edit source]
This page describes the mechanical characteristics of the ETRA SBC board.
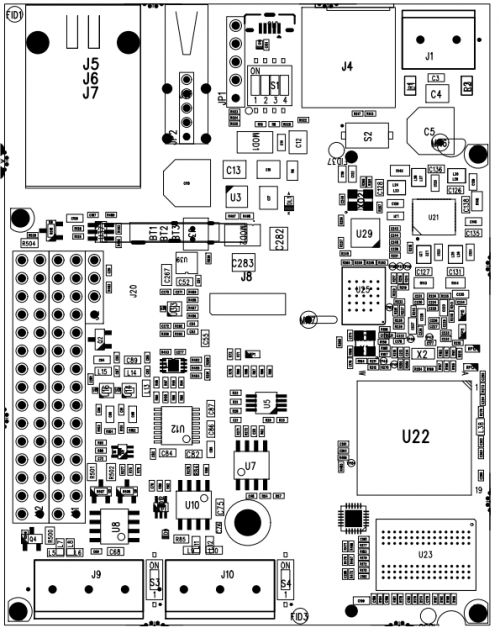
Board layout[edit | edit source]
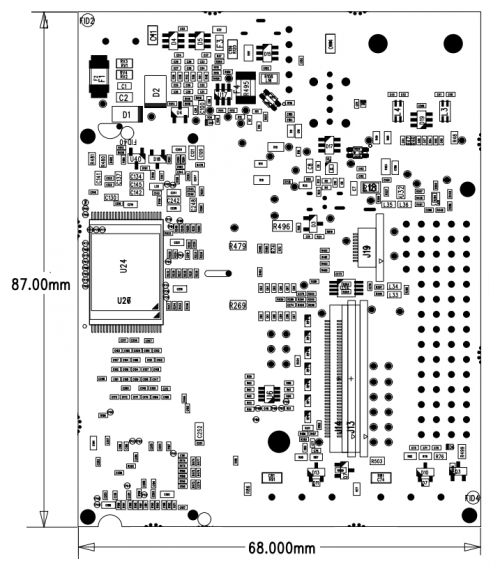
Dimensions[edit | edit source]
3D drawings[edit | edit source]
Mechanical data[edit | edit source]
| Dimension | Value |
|---|---|
| Width | 87 mm |
| Depth | 68 mm |
| Max component's height (top) | - mm |
| Max component's height (bottom) | |
| PCB height | - mm |